- 简单凯撒,偏移量为1
- 0xGame{The_Beginning_Of_Crypto}
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from hashlib import md5
def MD5(m):return md5(str(m).encode()).hexdigest()
Pub_Key = (689802261604270193, 620245111658678815)
e = Pub_Key[1]
n = Pub_Key[0]
p = 823642439
q = 837502087
c = 289281498571087475
d = inverse(e,(p-1)*(q-1))
m = pow(c,d,n)
flag = flag = '0xGame{'+ MD5(m) +'}'
print(flag)
- 0xGame{5aa4603855d01ffdc5dcf92e0e604f31}
- 逆向,编写脚本
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from base64 import b64decode
m0 = b'0xGame{73d7'
m1 = 60928972245886112747629873
m2 = '3165662d393339332d3034'
m3 = b'N2YwZTdjNGRlMX0='
m1 = long_to_bytes(m1)
m2 = bytes.fromhex(m2)
m3 = b64decode(m3)
print(m0+m1+m2+m3)
- 0xGame{73d72f64-7656-11ef-9393-047f0e7c4de1}
- 由脚本可以知道key长度为5,恰巧0xGame正好五个字母
- 编写脚本可以得到key是oWccl
alpha1 = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
alpha2 = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
m = '0lCcop{oyd94092-g8mq-4963-88b6-4helrxdhm6q7}'
clue = '0xGame'
key = ''
for i in range(len(clue)):
if clue[i] in alpha1:
key += alpha1[(alpha1.find(m[i])-alpha1.find(clue[i]))%26]
elif clue[i] in alpha2:
key += alpha2[(alpha2.find(m[i])-alpha2.find(clue[i]))%26]
print(key)
- 后续可以使用工具,或者使用脚本
alpha1 = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
alpha2 = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
m = '0lCcop{oyd94092-g8mq-4963-88b6-4helrxdhm6q7}'
key = 'oWccl'
key_nums = []
pointer = 0
ans = ''
for i in key:
if i in alpha1:
key_nums += [alpha1.find(i)]
elif i in alpha2:
key_nums += [alpha2.find(i)]
for i in m:
if i in alpha1:
new_index = (alpha1.find(i) - key_nums[pointer]) % 26
ans += alpha1[new_index]
pointer = (pointer + 1) % len(key_nums)
elif i in alpha2:
new_index = (alpha2.find(i) - key_nums[pointer]) % 26
ans += alpha2[new_index]
pointer = (pointer + 1) % len(key_nums)
else:
ans += i
print(ans)
- 得到0xGame{acb94092-e8bc-4963-88f6-4fcadbbfb6c7}
- 写脚本
from Crypto.Util.number import *from hashlib import md5
def MD5(m):return md5(str(m).encode()).hexdigest()
Pub_Key = (547938466798424179, 80644065229241095)
Prv_Key = (547938466798424179, 488474228706714247)
Encrypt_msg = 344136655393256706
m = pow(Encrypt_msg,Prv_Key[1],Prv_Key[0])
flag = '0xGame{'+ MD5(m) +'}'
print(flag)
- hint提示CRT中国剩余定理和二次剩余
二次剩余: 二次剩余(Quadratic Residue)是数论中的一个概念。简单来说,如果一个整数 𝑥的平方模 𝑛结果等于某个整数 𝑎,那么这个 𝑎就称为模 𝑛的一个二次剩余。
- 注意到
print(gmpy2.gcd(e,phi))的输出是2,也就是说令$e'=\frac{e}{2}$有$(m^\left. e'\right. )^2\equiv c\ mod\ n$ - 要求解任意模数二次剩余先要 求解奇素数模数二次剩余 -具体理论查看此链
- 据此推导过程编写脚本
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from hashlib import md5
import gmpy2
import sympy
from sympy.ntheory.modular import crt
def MD5(m):return md5(str(m).encode()).hexdigest()
Pub_Key = (1022053332886345327, 294200073186305890)
c = 107033510346108389
e = Pub_Key[1]
n = Pub_Key[0]
p = 970868179
q = 1052721013
phi = (p-1) * (q-1)
print(gmpy2.gcd(e,phi)) # 发现公约数2,分析得到二次剩余
def find_quadratic_residues(a, p):
# 首先检查 a 是否是模 p 下的二次剩余
if not sympy.is_quad_residue(a, p):
return None # 如果 a 不是二次剩余,返回 None
# 使用 sympy 的 nthroot_mod 找到一个解
x = sympy.nthroot_mod(a, 2, p, all_roots=False)
# 计算另一个解
second_solution = p - x
return (x, second_solution)
x1 = find_quadratic_residues(c,p) # 求解模p下的二次剩余
x2 = find_quadratic_residues(c,q) # 求解模q下的二次剩余
for i in x1:
for j in x2:
remainders = [i,j]
mods = [p,q]
m_ = crt(mods, remainders)[0] # CRT合并得到模n的二次剩余解
c_ = m_%n
e_ = e//2
d = inverse(e_,phi)
m = pow(c_,d,n)
flag = '0xGame{'+ MD5(m) +'}'
print(flag)
- 注意的是,对于求解二次剩余有两解,所以在合并的时候都可以作为合并用的解
- 所以遍历所有组合,得到正确flag
- 0xGame{127016d0be858ef48a99723710ad4d49}
- Diffie-Hellman题目是一个很好的hint,去了解了一下
- 这是一种公钥交换的算法,在A,B两人处各自生成一对密钥(A,a)和(B,b)
- 其中A和B是公钥用来互相间传输的,a和b是私钥,保存在本地
- 然后两人用自己的私钥和对方的公钥就可以生成出S(共享公钥),两人计算出来的S是相同的
- 然后查看题目附件,就是在靶机上生成(A,a),并发送A
- 那本地为了能建立通信,同样也生成(B,b),并发送B。(此处生成过程可以套用附件的函数)
- 此时靶机便会计算出S,继而计算出MD5,并以此用作AES加密的密钥
- 最终输出密文
- 那本地同样用b和A生成S,然后用自带库AES解密密文
- 编写脚本
from string import ascii_letters, digits
from hashlib import sha256
from itertools import product
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from hashlib import md5
from pwn import *
ip = '118.195.138.159' #要netcat的ip
port = 10000 #端口
io = remote(ip,port)
def proof():
io.recvuntil(b'XXXX+')
proof = io.recvuntil(b')')[:-1]
io.recvuntil(b'== ')
hash = io.recvuntil(b'\n')[:-1].decode()
dict = ascii_letters + digits
for word in product(dict, repeat=4):
word = ''.join(word).encode()
if sha256( (word+proof) ).hexdigest() == hash: break
io.sendlineafter(b'XXXX: ',word)
def MD5(m):return md5( str(m).encode() ).digest()
proof()
q,g = io.recvline().decode()[15:-2].split(", ")
q,g = int(q),int(g)
Bob_PriKey = randint(1, q)
Bob_PubKey = pow(g, Bob_PriKey, q)
Alice_PubKey = int(io.recvline().decode()[15:-1])
print(f"Alice_PubKey={Alice_PubKey}")
io.recvuntil(b"[+] Give me the Bob_PubKey\n>")
io.sendline(str(Bob_PubKey).encode('utf-8'))
io.recvline()
c = io.recvline().decode()[17:-1]
Share_Key = pow(Alice_PubKey,Bob_PriKey,q)
Cipher = AES.new(MD5(Share_Key), AES.MODE_ECB)
m = Cipher.decrypt(bytes.fromhex(c))
print(m.strip(b"\x00"))
- 0xGame{107c7960-d339-48b5-92b9-d59ad5644cf6}
- 本题有关Elgamal数字签名
有关Elgamal数字签名
1. 系统初始化
选择一个大素数$p$和一个生成元$g$(通常是$g$是$p$的原根)。然后选择一个私钥$x$,满足
$p$ $g$ $y = g^xmod\ p$
2. 签名生成
要签署消息$m$,执行以下步骤:
- 哈希消息 :使用安全的哈希函数(如SHA-256)计算消息的哈希值$H(m)$。
- 选择随机数 :选择一个随机数$k$,满足$1<k<p−1$且$k$与$\varphi(p) = p-1$互质。
- 计算签名 :
- 计算$r = g^k mod\ p$。
- 计算$s = k^{-1} \cdot (H(m) + x \cdot r) mod (p-1)$,其中$k^{-1}$是$k$模$\varphi(p)$的逆元。
签名为$(r,s)$。
3. 签名验证
接受放在接收到消息$m$和$(r,s)$后,可以通过以下步骤验证签名
- 验证$r$的有效性 :检查$0<r<p$和$0<s<p−1$是否成立。
- 计算哈希值 :计算$H(m)$
- 计算验证值 :
- 计算$u_1=y^rr^smod\ p$。
- 计算$u_2=g^mmod\ p$。
- 验证签名 :如果$u_1=u_2\ mod\ p$,则签名有效,否则无效。
- 题干有明显提到在验签函数中参数校验出现问题
- 检查发现,$(r,s)$是对$q$取模后的结果
- 然而在验签中并没有校验$r$和$s$的大小,也就是说,我可以传入比$q$大的数
- 这里就存在了伪造签名的可能性
- 然而Elgamal并不是直接对明文加密,而是对其的sha256加密
- 由于目前sha256的不可碰撞性,和无法预知性,并不能推测出伪造明文$m'$
- 因而要依据$m$和$m'$的关系进行推算得到$r'$和$s'$
- 以下为推导过程
- 然后手写脚本,逆元计算k
from string import ascii_letters, digits
from hashlib import sha256
from itertools import product
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from pwn import *
ip = '118.195.138.159' #要netcat的ip
port = 10002 #端口
io = remote(ip,port)
def proof():
io.recvuntil(b'XXXX+')
proof = io.recvuntil(b')')[:-1]
io.recvuntil(b'== ')
hash = io.recvuntil(b'\n')[:-1].decode()
dict = ascii_letters + digits
for word in product(dict, repeat=4):
word = ''.join(word).encode()
if sha256( (word+proof) ).hexdigest() == hash: break
io.sendlineafter(b'XXXX: ',word)
proof()
q,g,y = io.recvline().decode()[23:-2].split(", ")
q,g,y = map(int,[q,g,y])
phi = q-1
msg = bytes.fromhex(io.recvline().decode()[16:-1])
r,s = io.recvline().decode()[28:-2].split(", ")
r,s = map(int,[r,s])
io.recvuntil(b"Now, it's your turn to help me sign something\n[+] Give me your message:\n>")
msg_ = (b'Welcome_to_0xGame2024').hex()
io.sendline(msg_.encode('utf-8'))
msg_ = bytes.fromhex(msg_)
m = int(sha256(msg).hexdigest(),16)
m_ = int(sha256(msg_).hexdigest(),16)
k = m_*inverse(m,(q-1))
s_ = k*s
k1 = (k-1)*r//q+(k-1)*r%q
k2 = (k-1)*r%q
r_ = r+k1*q
io.recvuntil(b"[+] Give me your r:\n>")
io.sendline(str(r_).encode('utf-8'))
io.recvuntil(b"[+] Give me your s:\n>")
io.sendline(str(s_).encode('utf-8'))
io.interactive()
- 0xGame{93e9adb8-8a6d-4517-9c61-13081c413e41}
- 分析代码发现,在util文件中定义了由密钥KEY生成密钥流keystream
- 以及异或加密
- 用脚本连接靶机通过人机验证
from string import ascii_letters, digits
from hashlib import sha256
from itertools import product
from pwn import *
ip = '118.195.138.159' #要netcat的ip
port = 10001 #端口
io = remote(ip,port)
def proof():
io.recvuntil(b'XXXX+')
proof = io.recvuntil(b')')[:-1]
io.recvuntil(b'== ')
hash = io.recvuntil(b'\n')[:-1].decode()
dict = ascii_letters + digits
for word in product(dict, repeat=4):
word = ''.join(word).encode()
if sha256( (word+proof) ).hexdigest() == hash: break
io.sendlineafter(b'XXXX: ',word)
proof()
io.interactive()
- 输入明文获取对应的密文,以及flag的密文
- 注意:因为密钥流是256长度随机生成,所以输入明文必须比flag长,才能计算出加密时使用过的密钥
- 编写脚本计算flag
m = "6162636465666768696a6b6c6d6e6f707172737475767778797a6162636465666768696a6b6c6d6e6f707172737475767778797a"
c = "1c2227967f1f7e60b38d47862cd1bf575075ac29b4108d2a7604e4368cc63b5f8d89d93701d6a26257f97da0952b15a5211d94d9"
enc = "4d380393771c6230ebd114d8728ce70a1730ec6cec5fcb313853e164d992730a8f87d3390cdffe6e59bc6aaf"
KEY = None
def recover_key(plaintext, ciphertext):
pt_bytes = bytes.fromhex(plaintext)
ct_bytes = bytes.fromhex(ciphertext)
keystream = bytes([b1 ^ b2 for b1, b2 in zip(pt_bytes, ct_bytes)])
return keystream
enc = bytes.fromhex(enc)
keystream = recover_key(m,c)
flag = bytes([b1 ^ b2 for b1, b2 in zip(enc, keystream)])
print(flag)
- 此处的输入我用了[a-zA-Z]
- 最终得到0xGame{81682337-6731-91c7-d060-3efcdfe1ba5f}
- 都是常见的RSA攻击类型,BUUCTF全刷到过,查看原理以及之前的wp
- 主要不想手动解,便花了点时间用pwntool写了个自动脚本
- challenge1是低加密指数攻击
- challenge2是dp泄露
- challenge3是维纳攻击
- challenge4是共模攻击
from string import ascii_letters, digits
from hashlib import sha256
from itertools import product
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from RSAwienerHacker import *
import gmpy2
ip = '118.195.138.159' #要netcat的ip
port = 10003 #端口
io = remote(ip,port)
def proof():
io.recvuntil(b'XXXX+')
proof = io.recvuntil(b')')[:-1]
io.recvuntil(b'== ')
hash = io.recvuntil(b'\n')[:-1].decode()
dict = ascii_letters + digits
for word in product(dict, repeat=4):
word = ''.join(word).encode()
if sha256( (word+proof) ).hexdigest() == hash: break
io.sendlineafter(b'XXXX: ',word)
def slove0():
io.recvuntil(b"[+] input choice:\n>")
io.sendline(b'0')
n,e,c = io.recvline().decode()[1:-2].split(', ')
n,e,c = int(n),int(e),int(c)
# 低加密指数广播攻击
io.recvuntil(b">")
while True:
if gmpy2.iroot(c,e)[1]:
m = gmpy2.iroot(c,e)[0]
print(f"1:{m}")
break
c += n
io.sendline(str(m).encode('utf-8'))
def slove1():
io.recvuntil(b"[+] input choice:\n>")
io.sendline(b'1')
n,e,c,dp = io.recvline().decode()[1:-2].split(', ')
n,e,c,dp = int(n),int(e),int(c),int(dp)
# dp泄露
a = dp*e-1
for x in range(2,e):
if a%x == 0:
p = a//x+1
if n%p == 0:
q = n//p
break
d = inverse(e,(p-1)*(q-1))
m = pow(c,d,n)
print(f"2:{m}")
io.sendline(str(m).encode('utf-8'))
def slove2():
io.recvuntil(b"[+] input choice:\n>")
io.sendline(b'2')
n,e,c = io.recvline().decode()[1:-2].split(', ')
n,e,c = int(n),int(e),int(c)
# 维纳攻击
d = hack_RSA(e,n)
m = pow(c,d,n)
print(f"3:{m}")
io.sendline(str(m).encode('utf-8'))
def slove3():
io.recvuntil(b"[+] input choice:\n>")
io.sendline(b'3')
n,e,c,e_,c_ = io.recvline().decode()[1:-2].split(', ')
n,e1,c1,e2,c2 = int(n),int(e),int(c),int(e_),int(c_)
# 共模攻击
e1_e2=e1-e2
s1 = inverse(e1_e2,e2)
s2 = (1-e1*s1)//e2
m = pow(c1,s1,n)*pow(c2,s2,n)%n
print(f"4:{m}")
io.sendline(str(m).encode('utf-8'))
proof()
slove0()
slove1()
slove2()
slove3()
io.interactive()
- 最后拿到0xGame{2b5e024a-3c62-4f4a-afe0-b81851d9efc8}
- LFSR是指线性(Linear)反馈(Feedback)移位(Shift)寄存器(Register)
- 即有一个可移动的寄存器,通过反馈计算出下一个移动的数值,而其计算方式是线性的
- 分析源码得到存在一个mask固定窗口和state滑动窗口,最初始的state即为seed
- 两个列表中的二进制对应按位与运算,将所有结果异或保存至output
- output即为生成的随机数,存入getrandbits函数中的result末尾
- 将output存入state末尾,使窗口向后滑动一位
- 继续反复操作,不断生成随机数
- 注意到题目给的随机数是生成128位后的结果
- 因此可以判断,一组随机数生成后正好完全将原先128位的seed从state变量中顶出
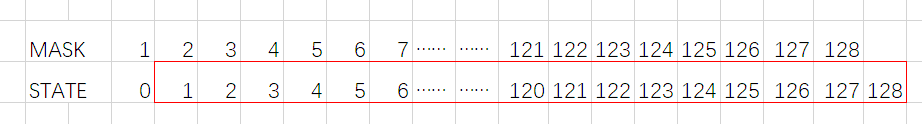
- 如图,假设这是最后一次生成随机数,计算时的mask是1
128,state是0127,上下同列的按位与运算,再异或,存入state的末尾(128)最终红色框内的128位数就是最终输出的随机数 - 也就是说,可以通过脚本算出state中0位置是什么,然后再反复使用这种方式计算出原来完整的128位seed
- 下面编写脚本
from hashlib import md5
def MD5(m):return md5(str(m).encode()).hexdigest()
def init_state(seed):
result = [int(i) for i in bin(seed)[2:]]
PadLenth = 128 - len(result)
result += [ 0 ] * PadLenth
assert len(result) == 128
return result
def init_random(seed):
result = [int(i) for i in bin(seed)[2:]]
PadLenth = 128 - len(result)
result = [ 0 ] * PadLenth + result
assert len(result) == 128
return result
random1 = 103763907686833223776774671653901476306
copy = random1
random2 = 136523407741230013545146835206624093442
Mask_seed = 245818399386224174743537177607796459213
random1,random2 = map(init_random,[random1,random2])
mask = init_state(Mask_seed)
def calc(state):
for i in range(128):
output = 0
for i in range(1,128):
output += state[i-1]*mask[i]
output += state[-1]
output = output%2
state = [output] + state[:-1]
return state
result = int(''.join(str(x) for x in calc(random2)),2) == copy
print(f"The calculation is {result}")
print("0xGame{"+MD5(int(''.join(str(x) for x in calc(random1)),2))+"}")
- 代码中要注意随机数的长度并没有128位要手动补零,同时是在开头补,而不是调用源码的方法
- 另外可以用第二个随机数来检验算法是否正确
- 运行得到0xGame{030ec00de18ceb4ddea5f6612d28bf39}
- 这题是依据种子和随机数倒推掩码
- mask用$x_1~x_128$表示
- seed用$s_1~s_128$表示
- random用$x_129~x_256$表示
- 可以得到如下的计算式
- 因此可以写出在Zmod 2数域下的矩阵
- 用Sage编写脚本计算解
from hashlib import md5
def MD5(m):return md5(str(m).encode()).hexdigest()
def init_state(seed):
result = [int(i) for i in bin(seed)[2:]]
PadLenth = 128 - len(result)
result += [ 0 ] * PadLenth
assert len(result) == 128
return result
def init_random(seed):
result = [int(i) for i in bin(seed)[2:]]
PadLenth = 128 - len(result)
result = [ 0 ] * PadLenth + result
assert len(result) == 128
return result
random1 = 299913606793279087601607783679841106505
random2 = 192457791072277356149547266972735354901
seed = 165943427582675380464843619836793254673
random1,random2 = map(init_random,[random1,random2])
seed = init_state(seed)
def solve_GF2_linear_system(A, b):
"""
使用 SageMath 在 GF(2) 上求解线性方程组 Ax = b
:param A: 系数矩阵
:param b: 结果向量
:return: 解向量 x
"""
F = GF(2)
A_GF2 = Matrix(F, A)
b_GF2 = vector(F, b)
try:
x = A_GF2.solve_right(b_GF2)
return x
except ValueError:
return None
def solution(m):
a,b = m[0],m[1]
solution = solve_GF2_linear_system(a, b)
if solution:
print(f"解向量为: {solution}")
return solution
else:
print("无解")
return None
def change(seed,random):
All = seed + random
a = [[0]*128 for _ in range(128)]
b = random
for i in range(128):
a[i] = All[i:i+128]
return (a,b)
ans1 = solution(change(seed,random1))
ans2 = solution(change(random1,random2))
print("The calculation is ",ans1 == ans2)
if ans1 == ans2:
print("0xGame{"+MD5(int("".join(str(i) for i in ans1),2))+"}")
- 解出0xGame{d56821feacab64cdb87c754ad06823a2}
- 椭圆曲线选择 :
- 首先,双方需要选定一条公共的椭圆曲线。椭圆曲线可以用方程
$y^2 = x^3 + ax + b \mod p$ 表示,其中$a$ 、$b$ 是曲线参数,$p$ 是素数,用于定义有限域上的曲线。 - 在这条曲线上,双方还需要选定一个公共点
$G$ ,称为基点。基点是椭圆曲线上的一个已知点,通信双方将用它来生成密钥。
- 密钥生成 :
-
Alice 随机生成一个私钥
$a$ ,这个私钥是一个整数。- 她计算对应的公钥
$A = a \cdot G$ ,这里的点乘是椭圆曲线点的标量乘法(多次加法运算)。
- 她计算对应的公钥
-
Bob 也生成一个随机的私钥
$b$ ,并计算出对应的公钥$B = b \cdot G$ 。
- 公钥交换 :
- Alice 将她的公钥
$A$ 发送给 Bob,Bob 将他的公钥$B$ 发送给 Alice。
- 共享密钥计算 :
-
Alice 使用她的私钥
$a$ 和 Bob 的公钥$B$ 计算共享密钥:$S = a \cdot B = a \cdot (b \cdot G) = (a \cdot b) \cdot G$ -
Bob 使用他的私钥
$b$ 和 Alice 的公钥$A$ 计算共享密钥:$S = b \cdot A = b \cdot (a \cdot G) = (b \cdot a) \cdot G$ - 由于点乘是交换的,Alice 和 Bob 最终计算得到相同的共享密钥
$S$ 。 - 很好理解啊,不涉及比较难的数学知识,只要搞懂原理就行,也用会算
- 和**[Week 2] Diffie-Hellman**逻辑上几乎一样,就是本地生成私钥和公钥,然后与靶机交互确定共享公钥
- 最终用AES对称加密来传输数据
- 上代码
from hashlib import md5, sha256
from itertools import product
from string import ascii_letters, digits
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from pwn import *
from Util import *
addr = "nc 118.195.138.159 10004".split(" ")
io = remote(addr[1],int(addr[2]))
def MD5(m):return md5( str(m).encode() ).digest()
def proof():
io.recvuntil(b'XXXX+')
proof = io.recvuntil(b')')[:-1]
io.recvuntil(b'== ')
hash = io.recvuntil(b'\n')[:-1].decode()
dict = ascii_letters + digits
for word in product(dict, repeat=4):
word = ''.join(word).encode()
if sha256( (word+proof) ).hexdigest() == hash: break
io.sendlineafter(b'XXXX: ',word)
proof()
a = 10809567548006703521
b = 9981694937346749887
p = 25321837821840919771
E = Curve(a, b, p)
g_x,g_y = map(int,io.recvline().decode()[15:-2].split(","))
a_x,a_y = map(int,io.recvline().decode()[20:-2].split(","))
G = Point(g_x,g_y,E)
A = Point(a_x,a_y,E)
b = randint(1, p)
B = b * G
io.sendlineafter(b"[+] Give me the Bob_PubKey.x\n>",str(B.x).encode('utf-8'))
Share_Key = b * A
Cipher = AES.new(MD5(Share_Key.x), AES.MODE_ECB)
io.recvline()
c = bytes.fromhex(io.recvline().decode()[21:-1])
m = Cipher.decrypt(c)
print(m)
io.interactive()
- 0xGame{71234da9-baf8-406e-9cc7-d08ceedea945}
- ECC加密用来交换对称密钥
- 可以发现素数p不是太大,于是尝试暴力计算key或k
- 实测k和key都能爆出来
- Sage脚本:Baby-step Giant-step 算法求解 ECDLP
# Sage 环境
def baby_step_giant_step(E, G, P, n):
"""
Baby-step Giant-step 算法求解椭圆曲线离散对数问题
E: 椭圆曲线
G: 基点
P: 已知点 P = k * G
n: 椭圆曲线的阶
"""
m = ceil(sqrt(n))
# Step 1: Baby-step, 计算表 {i: i*G} for i = 0, 1, ..., m-1
baby_steps = {}
for i in range(m):
baby_steps[i * G] = i
# Step 2: Giant-step, 计算 j * (-m * G)
inv_mG = -m * G
current = P
for j in range(m):
if current in baby_steps:
return j * m + baby_steps[current]
current += inv_mG
# 如果没有找到解,返回None
return None
# 椭圆曲线参数
p = 4559252311 # 椭圆曲线的素数域
a = 1750153947 # 椭圆曲线参数 a
b = 3464736227 # 椭圆曲线参数 b
E = EllipticCurve(GF(p), [a, b]) # 定义椭圆曲线
# 基点 G 和已知点 P = k * G
G = E(2909007728, 1842489211)
P = E(1923527223,2181389961)
# 椭圆曲线的阶
n = E.order()
# 使用 Baby-step Giant-step 求解 k
key = baby_step_giant_step(E, G, P, n)
if k is not None:
print(f"Found key: {key}")
else:
print("No solution found.")
- 得到
key = 1670419487 - 然后用内置的点乘计算$P = G' \cdot key$
- 再进行逆运算$M = C + ( - P')$
- 又可以根据定义可以知道$−Q=(x_Q,−y_Qmod\ p)$
- 所以搓脚本
from hashlib import md5
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Util import *
def MD5(m):return md5(str(m).encode()).digest()
p = 4559252311
a = 1750153947
b = 3464736227
curve = Curve(a, b, p)
G = Point(2909007728,1842489211,curve)
P = Point(1923527223,2181389961,curve)
G_= Point(1349689070,1217312018,curve)
C = Point( 662346568,2640798701,curve)
enc= bytes.fromhex("29bb47e013bd91760b9750f90630d8ef82130596d56121dc101c631dd5d88201a41eb3baa5aa958a6cd082298fc18418")
key = 1670419487
P_ = G_*key
M = C + Point(P_.x,(-P_.y)%p,curve)
Cipher = AES.new(MD5(M.x), AES.MODE_ECB)
m = Cipher.decrypt(enc)
print(m)
- 0xGame{0b0e28c2-b36d-d745-c0be-fcf0986f316a}
- 分析源码,要使输入的cookie能被正确解析为{"username": "admin", "time": ……}才能得到flag
- 分析发现对输入转化为json然后进行了AES.CBC加密,再以Base64输出
- 可以利用CBC加密特性,字节翻转攻击,定向改变某个解析后的明文
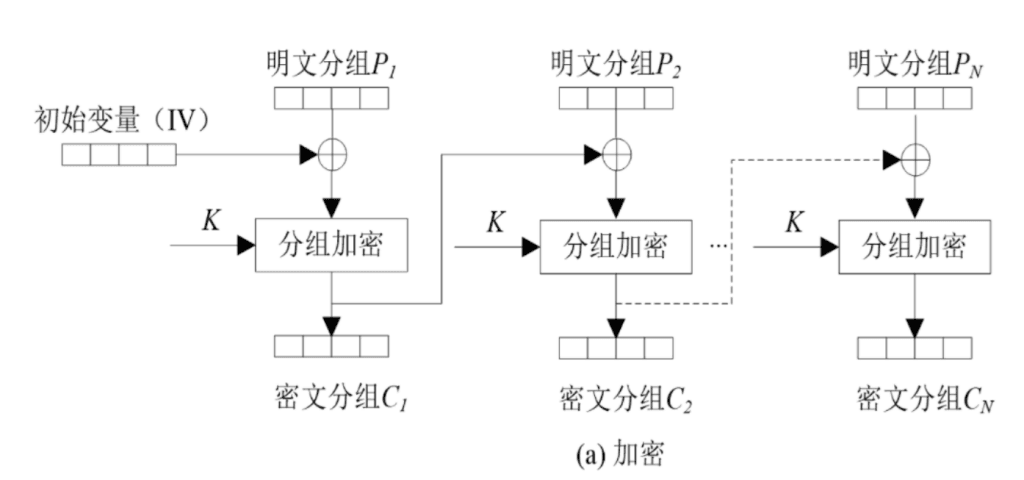
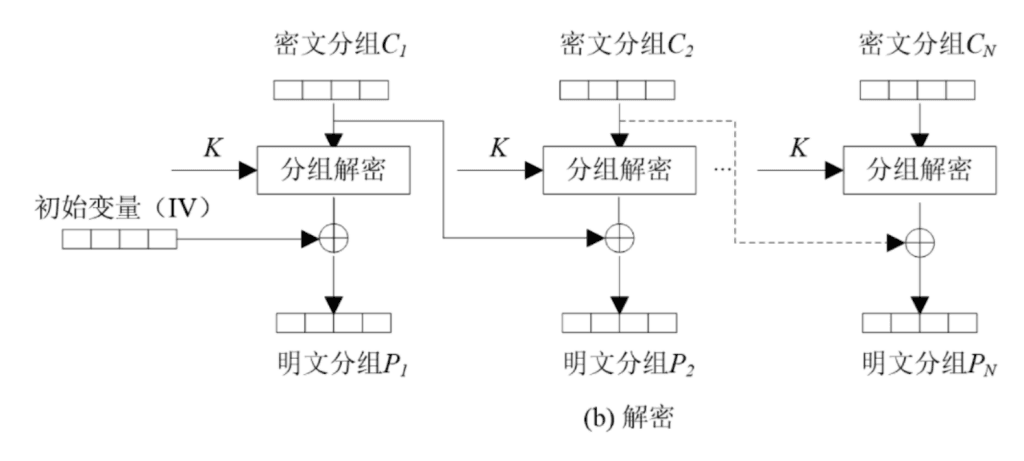
- 下面引用CBC加密和解密的图示
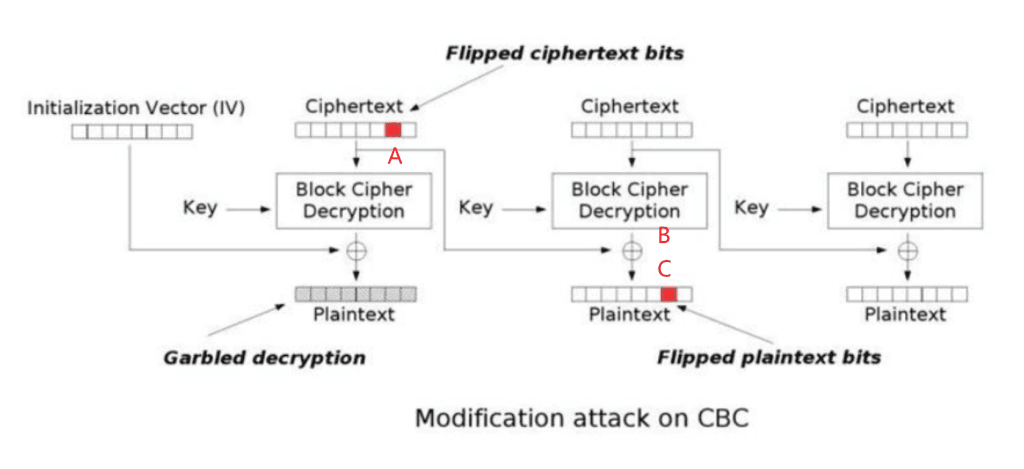
- 下面是反转攻击示例
- 由于C=B⊕A,可以特定改变A,使C变成想要的指定字符C'
- 推导得A’=A⊕C⊕C'
- 但要注意的是,虽然C被指定改变,但A的改变会影响到整段第一明文的变化
- 而json是格式固定的,也就意味着只能修改通过修改IV来修改第一明文,而无法改变第二明文
- 构造payload
from base64 import b64decode, b64encode
from pwn import *
addr = "nc 118.195.138.159 10005".split(" ")
io = remote(addr[1],int(addr[2]))
io.sendlineafter('''+--------------+
| [R] Regist |
| [L] Login |
| [F] Getflag |
+--------------+
[+] Tell me your choice:
>''',b"R")
io.sendlineafter("[+] username:\n>",b"zdmin")
base64en = io.recvline().decode()[13:]
base64de = bytearray(b64decode(base64en))
base64de[14] = base64de[14] ^ ord("z") ^ ord("a")
fake_cookie = b64encode(bytes(base64de))
io.sendlineafter("[+] Tell me your choice:\n>",b"L")
io.sendlineafter("[+] cookie:\n>",fake_cookie)
io.interactive()
- 0xGame{ad34acff-a813-4bc3-a44a-c270edf244b7}
- 在CBC加密的基础上,由于是分块处理,所以要对不能成块的部分进行填充
- 这里填充通常采用的是PKCS#7的标准进行填充,即填充字符个数与填充值相同,并且必须填充
- 如1234→1234\0x04\0x04\0x04\0x04
- 或12345678→12345678\0x08\0x08\0x08\0x08\0x08\0x08\0x08\0x08
- (上述是对于8个字节分块的情况举例)
- 下面讲述Padding Oracle Attack(或者CTF Wiki会比我更详细)
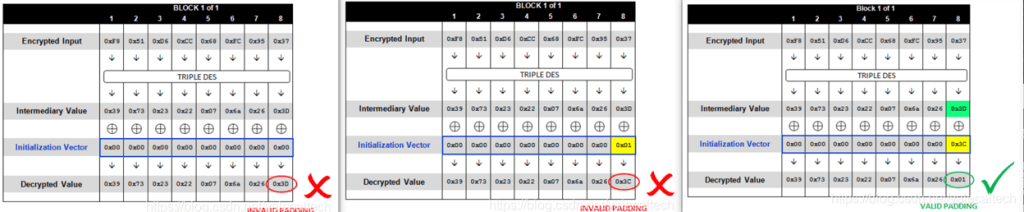
- 参考上一题的解密方式能发现
- 由于Block i在经过key解密后要和Block i-1异或得到Plaintxt
- 也就是说可以改变Block i-1的值来改变Plaintxt的结果,这都是上一题已知的
- 这题由于对明文脱padding的方法unpad中有Unpad error的报错
- 可以通过构造Block i-1的最后一个字节使得Plaintxt中的最后一个字节为\0x01
- 可以发现这样是不会报错的,而其他不正确的填充则会报错
- 所以可以通过靶机的回显来判断构造是否正确,从而得到正确明文(已知假明文,假IV可以推出中间值,与真IV异或后得到真明文)
- 然后再对倒数第二个字节同样方式爆破
- 注意:这里要保证爆破字节以外的字节满足假明文为\0x02
- 明白原理后就可以手搓脚本了
from base64 import b64decode, b64encode
from pwn import *
addr = "nc 118.195.138.159 10005".split(" ")
io = remote(addr[1], int(addr[2]))
io.sendlineafter('''+--------------+
| [R] Regist |
| [L] Login |
| [F] Getflag |
+--------------+
[+] Tell me your choice:
>''', b"F")
base = io.recvline().decode()[20:]
enc = b64decode(base)
io.sendlineafter("[+] Tell me your choice:\n>", b"L")
alpha = [4]
for i in "0123456789abcdef-}{xGame":
alpha += [ord(i)]
def padding_oracle_attack(ciphertext):
# 分块
blocks = [ciphertext[i:i + 16] for i in range(0, len(ciphertext), 16)]
decrypt = []
for block_index in range(1,len(blocks))[::-1]:
# 构造IV和密文块
current_block = blocks[block_index]
iv = blocks[block_index-1]
fake_iv = bytearray(iv)
# 遍历IV块
for attack_index in range(1,17):
# 伪造IV块中先前值
for change_index in range(1,attack_index):
fake_iv[-change_index] = fake_iv[-change_index] ^ (attack_index-1) ^ attack_index
# 遍历字节值
for bytes_value in range(1,256):
fake_iv[-attack_index] = bytes_value
print(f"尝试: bytes_value: {bytes_value:3}, fake_iv: {fake_iv.hex()}")
print(f"已得: {decrypt}\n")
if sendtest(fake_iv + current_block):
if (attack_index ^ bytes_value ^ iv[-attack_index]) in alpha:
decrypt += [attack_index ^ bytes_value ^ iv[-attack_index]]
break
return "".join([chr(i) for i in decrypt])
def sendtest(modified_ciphertext):
# 测试靶机响应
encoded_ciphertext = b64encode(modified_ciphertext).decode()
io.sendlineafter("[+] cookie:\n>", encoded_ciphertext)
resp = io.recvline().decode()
print("响应:", resp[:-1])
return resp != "[!] Unkown Wrong\n"
# 执行 padding oracle 攻击
decrypted = padding_oracle_attack(enc)[::-1]
print("解密结果: ", decrypted)
io.close()
注意几个点
- 原码在经过unpad之后有decode的处理,所以说不能转化为字符的字节同样会引发Unkown Wrong的报错,所以构造IV的时候不要用随机值或者全0填充
- 由于直接认定flag是uuid格式并且是由\0x04填充的,所以可以写入alpha,来避免其他同样可能满足不报错的可能性。(正常来说对于末尾字节会有多种可能,若当前可能无法继续往下爆破的时候,需要代码处理好回退操作。)
- 靶机测试响应中,有可能会成功json load从而触发TypeError Wrong报错,因此直接判断是否为Unkown Wrong即可
- 0xGame{6e02937e-634d-4f6f-8ef6-e5f387006cde}
速度很快,用了明文攻击,来自三顺七
from pwn import *
from base64 import b64encode, b64decode
from time import time
#context(log_level = 'debug')
s = time()
xor = lambda a, b: bytes([x^y for x, y in zip(a, b)])
io = remote('118.195.138.159', 10005)
io.sendlineafter(b'>', b'R')
io.sendlineafter(b'>', b'Admin')
io.recvuntil(b'[+] cookie : ')
cookie = io.recvline()[:-1]
prefix = b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x20\x00'
cookie = xor(b64decode(cookie), prefix) + b64decode(cookie)[16:]
io.sendlineafter(b'>', b'L')
io.sendlineafter(b'>', b64encode(cookie))
print(io.recvline().decode())
def Send(payload):
io.sendlineafter(b'>', b64encode(payload))
result = io.recvline()
#print(result)
if result == b'[!] Unkown Wrong\n':
return 0
elif result == b'[!] JSON Wrong\n':
return 1
elif result == b'[!] TypeError Wrong\n':
return 1
def PaddingOracle(before,after):
d_iv = [0 for _ in range(16)]
dict = list(b'0123456789abcdef{}xGame-') + [i for i in range(2, 16)]
print(f'dict = {dict}')
for i in range(1, 17):
flag = 1
Pad = [0 for _ in range(17-i)]
if i == 1:
Index = []
else:
Index = [i for _ in range(i-1)]
Prefix = Pad + Index
for j in dict:
d_iv[-i] = j ^ i
IV = bytes(xor(xor(before,d_iv), Prefix))
payload = IV + after
result = Send(payload)
if result == 1:
d_iv[-i] = j
flag = 0
print(i, d_iv)
break
if flag == 1:
for j in dict[::-1]:
d_iv[-(i-1)] = j ^ i
IV = bytes(xor(xor(before,d_iv), Prefix))
payload = IV + after
result = Send(payload)
if result == 1:
d_iv[-(i-1)] = j
print(i, d_iv)
break
for j in dict:
d_iv[-i] = j ^ i
IV = bytes(xor(xor(before,d_iv), Prefix))
payload = IV + after
result = Send(payload)
if result == 1:
d_iv[-i] = j
flag = 0
print(i, d_iv)
break
return bytes(d_iv)
def Oracle():
io.sendlineafter(b'>', b'F')
io.recvuntil(b'[+] Here is flag2 : ')
enc = io.recvline()
print(enc)
msg = b64decode(enc)
io.sendlineafter(b'>', b'L')
result = b''
BlockLength = len(msg)//16
print(f'[+] BlockLength = {BlockLength}')
Block = [msg[16 * i: 16 * (i+1)] for i in range(BlockLength)]
for i in range(0,BlockLength - 1):
print(f'[x] Procing BlockIndex : {i}')
result += PaddingOracle(Block[i], Block[i+1])
return result
flag2 = Oracle()
print(flag2)
io.close()
e = time()
print(f'[+] Cost : {e-s}')
- 原理比较难搞(我不会
- 题干说LLL算法出来就行,所以写如下sage
from sage.all import *
B = Matrix(ZZ, [[1849784703482951012865152264025674575, 2664848085955925754350117767673627932, 2099783527396520151610274180590854166, 1020558595577301617108111920545804527],
[1207449566811121614020334020195802372, 1954621976999112878661150903673543232, 1326050406731534201574943690688237338, 1361813208094227445768111591959011963],
[888810907577479776819993141014777624 , 1216302736807928240875874427765340645, 1027359437421599069599327712873719567, 238961447144792739830554790892164336 ],
[60622164517940943037274386912282 , 82958508138755168576836012717468 , 70072118066826856564329627650828 , 16296740862142507745322242235326 ]])
print(B.LLL())
- 由于flag混入在第一行,得到矩阵后取第一行,无视正负就是flag
- (由于LLL算出来的是最短基向量,而正负不会影响最短的特性)
- 脚本
from Crypto.Util.number import *
c = [ -58596440058654765094286903, -69377248846131264731819316, -60910008503494441471652194, -58497746791226042414948989]
print("".join([(long_to_bytes(abs(i))).decode() for i in c]))
- 0xGame{04679c42-2bc1-42b2-b836-1b0ca542f36b}
后续补充的原理
-
$CM=S$ 由于$||M||=1$可以认为$C$与$S$是等价的 - 而又由于$C$是随机生成的其施密特正交化程度几乎可以认为是 最高 -随机矩阵正交性的证明
- 因此对$S$进行LLL算法求其等价正交格基就等于求$C$
参考HNP讲解
- 基于LCG的生成规律$X_{n+1}=aX_n+b\ mod\ m$
- 已知如下式子
$$ \left{\begin{align} Cs[0]&=aseed\ mod\ m\ Cs[1]&=aCs[0]+b_1\ mod\ m\ Cs[i]&=aCs[i-1]+b_i\ mod\ m\ b_i&=Cs[i]-aCs[i-1]+k_i*m\ \end{align}\right. $$
- 然后构造格
$$
\begin{array}
(k_1&k_2&k_3&k_4&-a&1)
\left[\matrix{
m&0&0&0&0&0\
0&m&0&0&0&0\
0&0&m&0&0&0\
0&0&0&m&0&0\
Cs[0]&Cs[1]&Cs[2]&Cs[3]&K/n&0\
Cs[1]&Cs[2]&Cs[3]&Cs[4]&0&K
} \right] = (b_1&b_2&b_3&b_4&K\cdot a/m&K) \end{array} $$
- 其中$K$是$b_i$的估计值令$K=2^{128}$
- 然后就可以根据构造的格,来用sage求解
from Crypto.Util.number import *
cs = [
11804527453299586684489593808016317337345238230165321056832279785591503368758306671170625597063579251464905729051049524014502008954170088604924368057540940, 4930922884306486570759661288602557428608315558804950537470100263019228888817481617065454705843164809506859574053884206133344549895853064735361336486560981, 5380263856446165449531647111260010594620416730932539097782399557603420658350407080366132490174060420530708293564252852668431923560882648691392446521188465, 10746696290782998433216934286282230556131938525513632178308443345441147075710552571129957873399395862207656161609046567289600084193860244770966610161184627, 2195032957511830992558961021566904850278796737316238566513837995297394215638259916944087623923636789312134734949452839561765171446217520081402769962517110]
m = 12813864523019740432913161815051292412705285817864701047922722497269479288096574264414061282833203433542813637861620032851255308640850882149603687035724753
M = matrix(QQ,6,6)
for i in range(4):
M[i,i] = m
M[-2,i] = cs[i]
M[-1,i] = cs[i+1]
k=2^254
M[-2,-2]=k/m
M[-1,-1]=k
L=M.LLL()
print(L[0])
print(L[1])
print(L[2])
print(L[3])
print(L[4])
print(L[5])
res=L[1][-2].numerator()/k
a=abs(res)
print(a)
# 不知道为什么下面代码Sage中运行不了,但单独拎出来是可以运行的
from hashlib import md5
def MD5(m):return md5(str(m).encode()).hexdigest()
seed=cs[0]*inverse(a,m)%m
flag = '0xGame{' + MD5(seed) + '}'
print(flag)
- 0xGame{2db84757dd4197f9b9441be25f35bfd5}
- 没搞懂LLL但找到了板子
- 几乎一样,改改数据和移位
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from hashlib import md5
def MD5(m):return md5(str(m).encode()).hexdigest()
m = 181261975027495237253637490821967974838107429001673555664278471721008386281743
a = 80470362380817459255864867107210711412685230469402969278321951982944620399953
b = 108319759370236783814626433000766721111334570586873607708322790512240104190351
c = [2466192191260213775762623965067957944241015, 1889892785439654571742121335995798632991977, 1996504406563642240453971359031130059982231, 1368301121255830077201589128570528735229741, 3999315855035985269059282518365581428161659, 3490328920889554119780944952082309497051942, 2702734706305439681672702336041879391921064, 2326204581109089646336478471073693577206507, 3428994964289708222751294105726231092393919, 1323508022833004639996954642684521266184999, 2208533770063829989401955757064784165178629, 1477750588164311737782430929424416735436445, 973459098712495505430270020597437829126313, 1849038140302190287389664531813595944725351, 1172797063262026799163573955315738964605214, 1754102136634863587048191504998276360927339, 113488301052880487370840486361933702579704, 2862768938858887304461616362462448055940670, 3625957906056311712594439963134739423933712, 3922085695888226389856345959634471608310638]
h = [0] + c
length = len(h)
for i in range(length):
h[i] <<= 115
A = [1]
B = [0]
for i in range(1, len(h)-1):
A.append(a*A[i-1] % m)
B.append((a*B[i-1]+a*h[i]+b-h[i+1]) % m)
A = A[1:]
B = B[1:]
Ge = Matrix(ZZ,length,length)
for i in range(len(A)):
Ge[i,i] = m
Ge[-2,i] = A[i]
Ge[-1,i] = B[i]
K = 2**115
Ge[-2,-2] = 1
Ge[-1,-1] = K
for line in Ge.LLL():
if abs(line[-1]) == K:
L1 = line[-2]
seed1 = h[1] + L1
seed = (seed1 - b) * inverse(a,m) % m
print(f"seed = {seed}")
print('0xGame{' + MD5(seed) + '}')
- 0xGame{459049e068d93f6d70f1ea0da705264a}
- SIDH后量子安全密钥交换协议,嗐(学不懂
- 但是
- DH,说的很明白了,就是密钥交换
- 看源码发现只要模仿靶机生成密钥然后和靶机进行交互就可以了
- 实测:9.3版本代码无法正常运行,建议用10.4
- 抄靶机代码
from pwn import *
ea, eb = 110, 67
p = 2**ea * 3**eb - 1
F.<i> = GF(p**2, modulus=[1,0,1])
E0 = EllipticCurve(F, [1,0])
addr = "nc 118.195.138.159 10009".split(" ")
io = remote(addr[1],int(addr[2]))
recv = io.recvline().decode()[10:-2]
RA_ = re.split(r"\*i \+ |,", recv)
RA = E0(int(RA_[0])*i + int(RA_[1]), int(RA_[2])*i + int(RA_[3]))
print(f"RA={RA.xy()}")
PB = E0.random_point()
QB = E0.random_point()
sB = randint(0, 2**ea)
RB = PB + sB * QB
xy = [str(i).split("*i + ") for i in RB.xy()]
payload1 = ",".join(",".join(i) for i in xy)
print(f"RB={RB.xy()}")
print(f"payload1={payload1}")
phi_A = E0.isogeny(RA, algorithm='factored')
E_A = phi_A.codomain()
R_share = phi_A(PB) + sB * phi_A(QB)
phi_share = E_A.isogeny(R_share, algorithm='factored')
secret = phi_share.codomain().j_invariant()
payload2 = ",".join(i for i in str(secret).split("*i + "))
print(f"secret={secret}")
print(f"payload2={payload2}")
io.sendlineafter("[+] Give me RB:\n>",payload1.encode())
io.sendlineafter("[+] Tell me the secret\n>",payload2.encode())
flag = io.recvline()
print(flag)
io.interactive()
- 可能要多跑几次,因为secret出现整数的可能性还是挺大的(不知道为什么
- 0xGame{4179c8c3-db69-4fb0-bd14-ef6c76ddb973}
- 这是一个32位的MT19937伪随机数生成器
- 真实原理没怎么搞懂还是移步Cryptography wiki吧,那里比较详细
- 源码分析主要是三个操作,一个是在类生成时候的init初始化
- 二是624一组过后的twist旋转,在生成第一个数之前也经过旋转
- 三是每次生成随机数的函数extract
- 第一步逆向可以看Cryptography wiki,后两步逆向我参考的是独奏の小屋
- 套模板
from pwn import *
import random
from sympy import invert
addr = "nc 118.195.138.159 10006".split(" ")
io = remote(addr[1],int(addr[2]))
io.recvline()
result = [int(i) for i in io.recvline().decode()[1:-2].split(", ")]
# 逆向MT19937
class MT19937Recover:
def unshiftRight(self, x, shift):
res = x
for i in range(32):
res = x ^ res >> shift
return res
def unshiftLeft(self, x, shift, mask):
res = x
for i in range(32):
res = x ^ (res << shift & mask)
return res
def untemper(self, v):
v = self.unshiftRight(v, 18)
v = self.unshiftLeft(v, 15, 0xefc60000)
v = self.unshiftLeft(v, 7, 0x9d2c5680)
v = self.unshiftRight(v, 11)
return v
def go(self, outputs, forward=True):
result_state = None
assert len(outputs) >= 624
ivals = []
for i in range(624):
ivals.append(self.untemper(outputs[i]))
if len(outputs) >= 625:
challenge = outputs[624]
for i in range(1, 626):
state = (3, tuple(ivals+[i]), None)
r = random.Random()
r.setstate(state)
if challenge == r.getrandbits(32):
result_state = state
break
else:
result_state = (3, tuple(ivals+[624]), None)
rand = random.Random()
rand.setstate(result_state)
if forward:
for i in range(624, len(outputs)):
assert rand.getrandbits(32) == outputs[i]
return ivals
# 逆向twist
def untwist(newState, flag: bool = True):
oldState = [0] * 624
for i in range(624 - 1, -2, -1):
x = newState[i] ^ newState[(i + 397) % 624]
if x & 0x80000000 == 0x80000000:
x ^= 0x9908b0df
x <<= 1
x |= 1
else:
x <<= 1
if i > -1:
oldState[i] |= x & 0x80000000
if i + 1 < 624:
oldState[i + 1] |= x & 0x7fffffff
if i == 227 and flag:
newState = list(newState[:227]) + oldState[227:]
return oldState
# 逆向__init__
def _int32(x):
return int(0xFFFFFFFF & x)
def invert_right(res,shift):
tmp = res
for i in range(32//shift):
res = tmp^res>>shift
return _int32(res)
def recover(last):
n = 1<<32
inv = invert(1812433253,n)
for i in range(623,0,-1):
last = ((last-i)*inv)%n
last = invert_right(last,30)
return last
mtc = MT19937Recover()
newstate = mtc.go(result)
oldstate = untwist(newstate)
seed = recover(oldstate[-1])
print(f"seed={seed}")
io.sendlineafter("[+] seed = ?\n>",str(seed).encode())
io.interactive()
- 0xGame{2569bd55-a14d-46d8-81f5-e1397e4be7bc}
- p.s. extract逆向还是比较好理解(博客讲的很清楚),其他两种操作就难理解了
- 这是RSA已知p高位攻击Factoring with High Bits Known
- 所以可以构造出p用sage求解小根
- 参考博客
n = 135500646574582511239845764710311769260801998982429500680171919823431178899526463566215834234383331374445093363969218810906991784569340270510936759183504496584225937614940086329775325893307453919055830270986601152002191368431527285285313669979358099782497422114870417519470053198217401297960844455029559146309
c = 41763956818640145556632229720626372656921875856507389014855753965024986594502113237270745517422792354256348958542864591249410500750410658988509136242435502259172258432676502846729088278202750721760451160668653746019965695721844819587671602925551448624324524027931677927410810126647175483982178300855471710099
e = 65537
p_high = 918578024558168836638919636090777586135497638818209533615420650282292168631485
for i in range(2**5):
p4 = p_high << 5 #这里需要先爆破5位,使得知道264位以后再恢复p
p4 = p4 + i
kbits = 248
p4 = p4 << kbits
R.<x> = PolynomialRing(Zmod(n))
f = x + p4
res = f.small_roots(X=2^kbits, beta=0.4, epsilon=0.01)
if res != []:
p = p4 + res[0]
print(p)
break
- 得到p之后常规解密文就行
- 0xGame{8f4c17cb-442a-49bd-830a-d16af225a5c5}