This repository contains code produced while taking CS50 Introduction to Artificial intelligence with Python course by Harvard's OpenCourseWare. This is year 2024 version of the course.
First week of the course covers: Search Problems, Depth-First Search, Breadth-First Search, Greedy Best-First Search, A* Search, Minimax Algorithm and Alpha-Beta Pruning.
The assignment is a program that determines how many degrees of separation apart two actors are. This is framed as a search problem where nodes are people and edges are movies actors have starred in.
Input data
The program takes in three .csv files:
people.csvcontains each person's id, name and year of birth.movies.csvcontains each movie's id, title and the year in which the movie was released.stars.csvcontains pairs of person id and movie id, establishing a relationship between actors and movies they have starred in.
and names of two actors whom the user wants to find the shortest path between.
Implementation
The solution uses a breath-first seach algorithm to find the shortest path between two actors. It returns a list of nodes in the path or None if there is no path between them.
Output data
The program outputs the number of degrees of separation and the shortest path.
$ python degrees.py large
Loading data...
Data loaded.
Name: Emma Watson
Name: Jennifer Lawrence
3 degrees of separation.
1: Emma Watson and Brendan Gleeson starred in Harry Potter and the Order of the Phoenix
2: Brendan Gleeson and Michael Fassbender starred in Trespass Against Us
3: Michael Fassbender and Jennifer Lawrence starred in X-Men: First Class
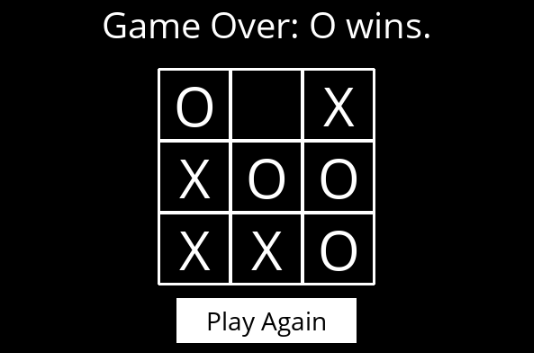
The assignment is to implement a program that plays Tic-Tac-Toe game optimally, using Minimax algorithm.
Input data
User interacts with the game's GUI by clicking into the cells where they want to place their next move.
Implementation
The game uses Minimax algorithm, as explained in the lecture.
Output data
The program outputs a GUI for the user to interact with. AI function acts as the opponent player, outputting its moves onto the GUI.
Second week of the course covers: Propositional Logic, Entailment, Inference, Model Checking, Resolution and First Order Logic.
The assignment is to develop a knowledge base that allows a pre-coded inference model to solve logic puzzles.
In 1978, logician Raymond Smullyan published “What is the name of this book?”, a book of logical puzzles. Among the puzzles in the book were a class of puzzles that Smullyan called “Knights and Knaves” puzzles.
In a Knights and Knaves puzzle, the following information is given: Each character is either a knight or a knave. A knight will always tell the truth: if knight states a sentence, then that sentence is true. Conversely, a knave will always lie: if a knave states a sentence, then that sentence is false.
The objective of the puzzle is, given a set of sentences spoken by each of the characters, determine, for each character, whether that character is a knight or a knave.
Input data
A logic puzzle is stated as series of statements that a character has said about themselves and/or other characters.
Implementation
The solution is a knowledge base in the form of propositional sentences for each logic puzzle. Each KB contains knowledge about the problem setup and the statements that each character has made.
Output data
The program outputs a solution to a given logic puzzle.
Puzzle 5
A is a Knave
B is a Knight
C is a Knight
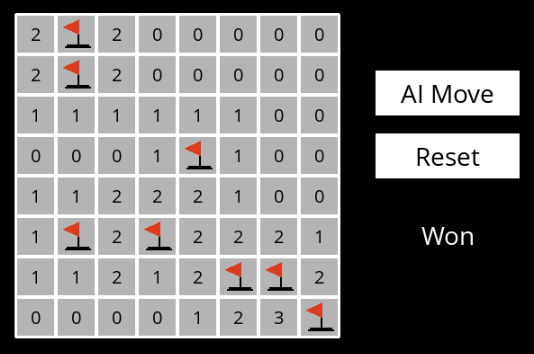
The assignment is a program that plays Mineweeper autonomously.
Input data
None. The program itself generates a game board of size 8 x 8 cells with 8 mines randmoly placed on it.
Implementation
The solution is a knowledge acquisition and model checking algorithm that infers safe moves for the AI player.
Output data
The program outputs a GUI. Every time when the user presses "AI Move" button, the program iterrates over the knowledge inferrable from the current state of the board, and makes a safe move. If there are no safe moves, the program makes a random move.
Third week of the course covers: Probability, Conditional Probability, Random Variables, Independence, Bayes' Rule, Joint Probability, Bayesian Networks, Sampling, Markov Models and Hidden Markov Models.
The assignment is two web-page ranking algorithms: Markov Chain random surfer algorithm and PageRank formula.
Input data
The program takes in:
- a corpus of web pages in a form of a python dictionary mapping each page to a set of all pages that are linked to by that page.
- a starting page.
- a damping factor representing the probability that the next page will be one of the pages that the current page links to (rather than a random page).
Implementation
The solution implements a Markov Chain sampling algorithm as describe here and PageRank formula as described here.
Output data
The program outputs probabilities for each page in the corpus that it will be the next page visited.
$ python pagerank.py corpus0
PageRank Results from Sampling (n = 10000)
1.html: 0.2223
2.html: 0.4303
3.html: 0.2145
4.html: 0.1329
PageRank Results from Iteration
1.html: 0.2202
2.html: 0.4289
3.html: 0.2202
4.html: 0.1307
The assignment is a Bayesian Network that can assess the likelihood that a person will inherit a gene or express a trait associated with that gene.
Input data
The program takes in:
- a .csv file specifying known information about each family member: their name, parents and whether or not they are expressing the trait.
- probabilities of various events: unconditional probability distribution of the gene in the population, conditional probability of expressing the trait when carrying a given number of genes (alleles) and probability of the gene mutatiting when inherited.
Implementation
The solution calculates the normalised joint probability of all possible events taking place, given the known events from the input.
Output data
The program outputs probabilities that each family member has the train gene and expresses the trait.
$ python heredity.py data/family0.csv
Harry:
Gene:
2: 0.0092
1: 0.4557
0: 0.5351
Trait:
True: 0.2665
False: 0.7335
James:
Gene:
2: 0.1976
1: 0.5106
0: 0.2918
Trait:
True: 1.0000
False: 0.0000
Lily:
Gene:
2: 0.0036
1: 0.0136
0: 0.9827
Trait:
True: 0.0000
False: 1.0000
Fourth week of the course covers: Local Search, Hill Climbing, Simulated Annealing, Linear Programming, Constraint Satisfaction and Backtracking Search.
The assignment is a program that fits words from a given dictionary to a pre-defined crossword pattern.
Input data
The program takes in a dictionary of words and an empty crossword puzzle structure.
Implementation
The solution is an optimisation problem where each word to be filled out in the crossword is a variable. Overlapping positions in the words are defined as constraints. The crossword is then solved by fitting the domain (the dictionary of all possible words) over the variables and their constraints.
Output data
The program outputs graphical representation of a filled out crossword puzzle.
$ python generate.py data/structure1.txt data/words1.txt output.png
██████████████
███████M████R█
█INTELLIGENCE█
█N█████N████S█
█F██LOGIC███O█
█E█████M████L█
█R███SEARCH█V█
███████X████E█
██████████████
Fifth week of the course covers: Supervised Learning, Nearest-Neighbor Classification, Perceptron Learning, Support Vector Machines, Regression, Loss Functions, Overfitting, Regularization, Reinforcement Learning, Markov Decision Processes, Q-Learning, Unsupervised Learning and k-means Clustering.
The assignment is an AI that predicts whether online shopping customers will complete a purchase.
Input data
The program takes in a .csv file with statistics about the user sessions on an e-commerce website, where each session is labeled whether or not it ended with a purchase.
Implementation
The program utilises scikit-learn library. The input dataset is split into training and validation data. The training data is then transformed and fed into a k-nearest-neighbours classifier to fit the model. Finally, the model is evaluated on the validation set.
Output data
The program outputs the statistics about the predictions the AI has made.
$ python shopping.py shopping.csv
Correct: 4088
Incorrect: 844
True Positive Rate: 41.02%
True Negative Rate: 90.55%
The assignment is an AI that teaches itself to play Nim through reinforcement learning.
Input data
The starting state is inherent in the rules of the game and pre-defined in the code. During gameplay user can input their move
Implementation
The solution implements a series of functions for Q-learning algorithm that associates reward values with particular actions carried out from particular states of the game board. The algorithm is then used to refine the reward values by running a series of simulated AI games against itself.
Output data
The program outputs notifications while training, and describes the game state and AI moves while playing the game against the user.
$ python play.py
Playing training game 1
Playing training game 2
Playing training game 3
...
Playing training game 9999
Playing training game 10000
Done training
Piles:
Pile 0: 1
Pile 1: 3
Pile 2: 5
Pile 3: 7
AI's Turn
AI chose to take 1 from pile 2.
Sixth week of the course covers: Artificial Neural Networks, Activation Functions, Gradient Descent, Backpropagation, Overfitting, TensorFlow, Image Convolution, Convolutional Neural Networks, Recurrent Neural Networks.
The assignment is a deep convolutional image classification neural network that identifies traffic signs in an image. In addition to code, extensive analysis of the optimal setup for the neural network was carried out.
Input data
The program accepts German Traffic Sign Recognition Benchmark (GTSRB) dataset of images of 43 traffic signs.
Implementation
The program uses tensorflow library with keras API. The solution is a convolutional neural network setup and
an algorithm for loading the input data into the array for training and evaluation. The neural network is trained for 10 epochs before validating the model.
Output data
The program outputs accuracy and loss metrics for all training epochs and the validation set.
$ python traffic.py gtsrb
Epoch 1/10
500/500 [==============================] - 5s 9ms/step - loss: 3.7139 - accuracy: 0.1545
Epoch 2/10
500/500 [==============================] - 6s 11ms/step - loss: 2.0086 - accuracy: 0.4082
Epoch 3/10
500/500 [==============================] - 6s 12ms/step - loss: 1.3055 - accuracy: 0.5917
Epoch 4/10
500/500 [==============================] - 5s 11ms/step - loss: 0.9181 - accuracy: 0.7171
Epoch 5/10
500/500 [==============================] - 7s 13ms/step - loss: 0.6560 - accuracy: 0.7974
Epoch 6/10
500/500 [==============================] - 9s 18ms/step - loss: 0.5078 - accuracy: 0.8470
Epoch 7/10
500/500 [==============================] - 9s 18ms/step - loss: 0.4216 - accuracy: 0.8754
Epoch 8/10
500/500 [==============================] - 10s 20ms/step - loss: 0.3526 - accuracy: 0.8946
Epoch 9/10
500/500 [==============================] - 10s 21ms/step - loss: 0.3016 - accuracy: 0.9086
Epoch 10/10
500/500 [==============================] - 10s 20ms/step - loss: 0.2497 - accuracy: 0.9256
333/333 - 5s - loss: 0.1616 - accuracy: 0.9535
Seventh week of the course covers: Syntax, Semantics, Context-Free Grammar, nltk, n-grams, Bag-of-Words Model, Naive Bayes, Word Representation, word2vec, Attention and Transformers.
The assignment is a program that parses sentences, determines their structure and extracts noun phrases.
Input data
The program accepts user input of sentences that consists of the words familiar to the model.
Implementation
The program uses ntlk library for natural language processing. The solution is a set of rules for parsing sentence semantic structure.
Output data
The program outputs a representation of the structure of the sentence.
$ python parser.py
Sentence: Holmes sat.
S
_____|___
NP VP
| |
N V
| |
holmes sat
Noun Phrase Chunks
holmes
The assignment is a natural language tokeniser that predicts a hidden word in a sentence, given the surrounding words. In addition to code, analysis of the attention heads was carried out.
Input data
The program accepts user input of a sentence with one masked word.
Implementation
The program uses transformers library with BERT langugage model. The solution is functionality for visualising the attention layers in the language model.
Output data
The program outputs theree most probable full sentences.
$ python mask.py
Text: We turned down a narrow lane and passed through a small [MASK].
We turned down a narrow lane and passed through a small field.
We turned down a narrow lane and passed through a small clearing.
We turned down a narrow lane and passed through a small park.
This description has been partially sourced from the CS50AI website. For education purposes only. No copyright infringement intended.
Plagiarism is strongly advised against. Please refer to the CS50's code of Academic Honesty if in doubt.