-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1.3k
GSoC Ideas
MNE-Python is planning to participate in the GSOC 2022 under the 🐍 Python Software Foundation (PSF) umbrella.
Note: If you are not currently pursuing research activities in MEG or EEG and do not use or do not plan to use MNE-Python for your own research, our GSoC might not be for you. Our projects require domain-specific interest and are not simple coding jobs.
MNE-Python is a pure Python package for preprocessing and analysis of M/EEG data. For more information, see our homepage.
For modes of communication see our getting help page. It's a good idea to introduce yourself on our Discourse forum to get in touch with potential mentors before submitting an application.
- MNE-Python must be in the title of your application!
- Student application information for Python
We list some potential project ideas below, but we welcome other ideas that could fit within the scope of the project!
Medium
350 hours
mne-qt-browser is a modern eletrophysiology browser based on Qt. It offers fast visualization of raw, epochs, and ICA time courses. However, there are many UI and usability improvements that could be added.
- Improve the overview bar
- Enable interactive switching between time courses and STFT/spectrogram view for individual traces, including UI elements to control various parameters (clim, cmap, n_fft, etc.)
- Add a two-control "time slider" and/or "channel slider" that allows setting the time span and channel span to show
- Optionally, add text overlays for each channel giving their value at the current time point (continuously updating)
- Add the possibility to load a file from the UI (add button or menu) or to simple drop a file in the window to view it
- Multiple other ideas on this project page
Medium
350 hours
We have an excellent 3D viewer for brain activations, and multiple ways of viewing evoked data (plot_topo, plot_topomap, plot_joint, etc.). We want to integrate these so that you can, for example, click on a time point in a Brain and have the evoked.plot_topomap update. This should be done using callbacks to allow for customizability.
- Design and implement a callback system for Brain and time-based viewers (plot_topo, plot_topomap, plot_joint, etc.)
- Provide a simple API for hooking
- Possibly allow passing an
(evoked, inv)pair to Brain to generate source time courses on the fly - Possibly allow integrating the
evoked.plot_*matplotlib figures into the brain viewer directly (this is a UI design problem mostly: should it use tabs, or something else?)
Hard
175 or 350 hours
MNE-Connectivity has some support for AR modeling of functional connectivity. This should ideally be expanded to support source-space modeling via a state-space (hidden variable) approach, and to support some graph statistical tests.
This is marked as "hard" because it requires a reasonable depth of domain-specific knowledge (autoregressive processes; some graph theory).
Any of the following would be helpful:
- Add tutorials on AR/state-space modeling, including some math primer/text
- Add a tutorial/simulation showing recovery of ground-truth from a few (2-3?) connected regions
- Add support for Yang 2016 state-space modeling (that incorporates a forward model and source labels; Yang 2016; some code here)
- Add Hotelling T2-based graph statistics (Ginestet 2017)
- Visualization functions for time-varying network directed/undirected connectivity
- Facilitate integration with graspologic via API to convert
*Connectivitytonetworkx-type data
175 or 350 hours
Medium (requires knowledge of M/EEG data)
Denis Engemann, Alex Gramfort, Eric Larson, Daniel McCloy
The aim of this project is to improve the access to open EEG/MEG databases via the mne.datasets module, in other words, improve our dataset fetchers. There is physionet, but much more. Having a consistent API to access multiple data source would be great.
See https://github.com/mne-tools/mne-python/issues/2852 and https://github.com/mne-tools/mne-python/issues/3585 for some ideas, or:
- MMN dataset (http://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/data/eeg_mmn/ ) used for tutorial/publications applying DCM for ERP analysis using SPM.
- Human Connectome Project Datasets (http://www.humanconnectome.org/data/ ). Over a 3-year span (2012-2015), the Human Connectome Project (HCP) scanned 1,200 healthy adult subjects. The available data includes MR structural scans, behavioral data and (on a subset of the data) resting state and/or task MEG data.
- Kymata Datasets (https://kymata-atlas.org/datasets). Current and archived EMEG measurement data, used to test hypotheses in the Kymata atlas. The participants are healthy human adults listening to the radio and/or watching films, and the data is comprised of (averaged) EEG and MEG sensor data and source current reconstructions.
- http://www.brainsignals.de/ A website that lists a number of MEG datasets available for download.
- BNCI Horizon (http://bnci-horizon-2020.eu/database/data-sets) has several BCI datasets
Medium (requires visualization and time-frequency analysis knowledge)
350 hours
Mainak Jas, Britta Westner, Sarang Dalal, Denis Engemann, Alex Gramfort, Eric Larson
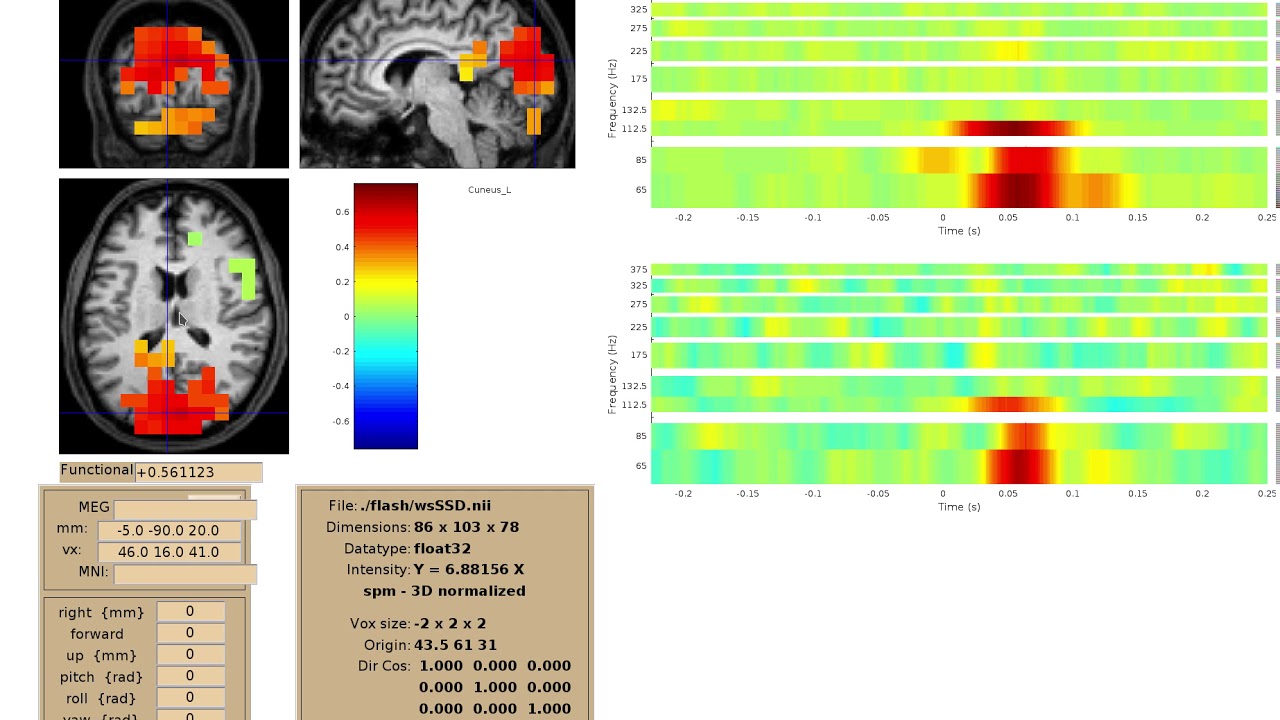
Implement viewer for interactive visualization of volumetric source-time-frequency (5-D) maps on MRI slices (orthogonal 2D viewer). NutmegTrip (written by Sarang Dalal) provides similar functionality in Matlab in conjunction with FieldTrip.
Example of NutmegTrip's source-time-frequency mode in action (click for link to YouTube):
- extend source time series (4-D) viewer created by Mainak Jas to a time-frequency (5-D) viewer
- Allow plotting surface data in volume using cortical ribbon (see closed glass brain PR: https://github.com/mne-tools/mne-python/pull/4496)
- capability to output source map animations directly as GIFs
- ability to plot on 3D rendered brains not necessary at this stage, but would be helpful if it is written such that it can be extended in the future
- extra credit: plot corresponding EEG/MEG topography at selected time point. (Not in video, but this can be done in NutmegTrip as well – very useful as a sanity check for source results.)
Medium (requires working with C++ bindings)
350 hours
OpenMEEG is a state-of-the art solver for forward modeling in the field of brain imaging with MEG/EEG. It solves numerically partial differential equations (PDE). It is written in C++ with Python bindings written in SWIG. The ambition of the project is to integrate OpenMEEG into MNE offering to MNE the ability to solve more forward problems (cortical mapping, intracranial recordings, etc.).
- Revamp Python bindings (remove useless functions, check memory managements, etc.)
- Write example scripts for OpenMEEG that automatically generate web pages as for MNE
- Package OpenMEEG for Debian/Ubuntu
- Update the continuous integration system