Matlab assignment for Spacecraft Subsystems course in MS Spacecraft Design at LTU Space Campus.
- Open the project in Matlab.
- Run
main_gui.mlapp.
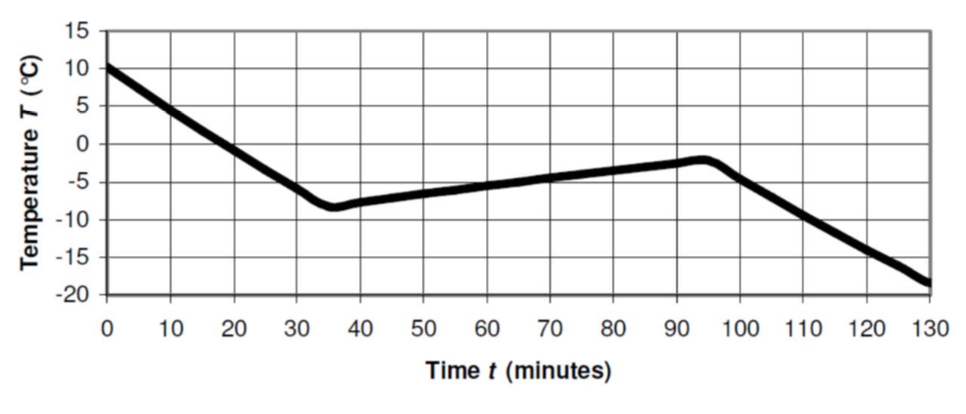
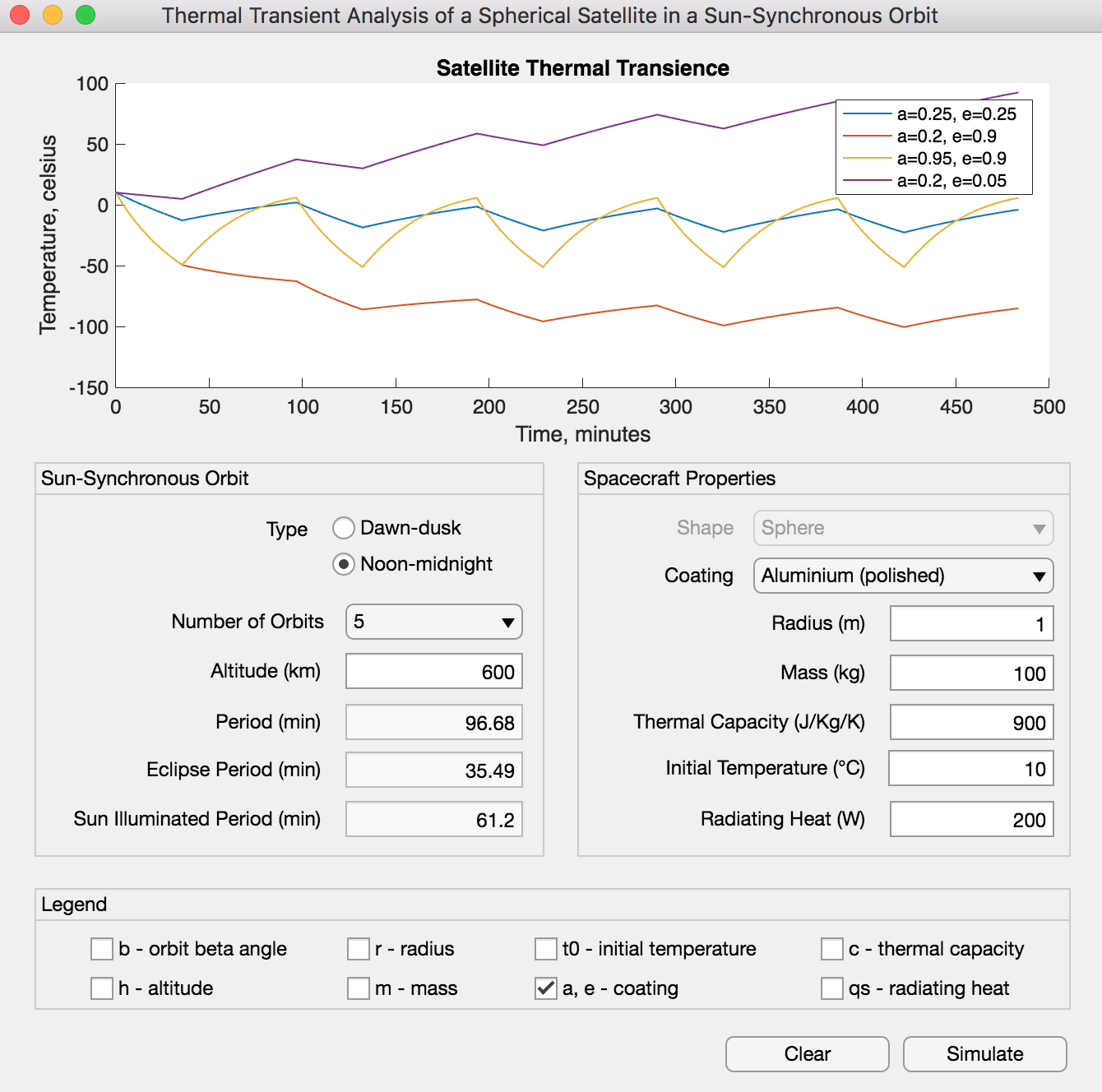
A spherical satellite is launched into a 600 km sun-synchronous noon-midnight orbit. It has a radius of r = 1 m, weighs 100 kg and is made of unpolished aluminium (alpha = 0.25, epsilon = 0.25, c = 900 J/kg K). An amplifier inside the spacecraft radiates hear at qs = 200 W. Calculate the temparature of the spacecraft as it enters eclipse, returns to sunlight, and goes through eclipse one more time. The initial temperature at the start of the sequence T0 = 10°C (283 K). The Stefan-Boltzmann constant sigma = 5.67^-8 W/m^2K^4. The earth's mean radius R = 6371 km.
Try to modify the code and simulate for longer periods in order to understand the behaviour once the system has reached a pseudo-stability condition.
Simulate the behaviour in Matlab and compare it with respect to the analytics solution in Berlin pp. 335:
- W.r.t changes of thermal capacity, describe the main effects when the thermal capacity is lower or higher than 900 J/kg°C.
- W.r.t changes of mass, describe the main effects when mass is lower or higher than 100 Kg (i.e. from 10 kg to 1000 kg).
- W.r.t changes of radius, describe the main effects when radius changes from 0.1 to 10 m.
- W.r.t. changes of internal heat, from 10 W to 1000 W.
- W.r.t. orbit altitude, from h = 200 km to 1000 km.