Yet Another Not So Obfuscated LLVM
Based on the release version 9.0.1. Other version might work as well, but one has to merge/rebase the X86 related code.
wget https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/releases/download/llvmorg-9.0.1/llvm-9.0.1.src.tar.xz
tar xf llvm-9.0.1.src.tar.xz && cd llvm-9.0.1.src
git init
git remote add origin https://github.com/emc2314/YANSOllvm.git
git fetch
git checkout -t origin/master -f
rm -rf .git
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -DLLVM_TARGETS_TO_BUILD="X86" ..
make
YANSOllvm operates on the IR level (and also X86 backend for obfCall). So first convert your source code to LLVM bytecode, e.g. clang -c -emit-llvm -O0 main.c -o main.bc.
Then you can apply passes to the bytecode:
{PATH_TO_BUILD_DIR}/bin/opt -load {PATH_TO_BUILD_DIR}/lib/LLVMObf.so -vm -merge -bb2func -flattening -connect -obfCon -obfCall main.bc -o main.obf.bc
Notice that the order of passes matters. You can use llvm's own passes or apply the same obfuscate pass twice, e.g. {PATH_TO_BUILD_DIR}/bin/opt -load {PATH_TO_BUILD_DIR}/lib/LLVMObf.so -vm -merge -O3 -bb2func -flattening -obfCon -connect -obfCon -obfCall main.bc -o main.obf.bc.
After that, compile the output bytecode to assembly using llc:
{PATH_TO_BUILD_DIR}/bin/llc -O3 --disable-block-placement main.obf.bc
Finally, assemble and link the output assembly:
clang main.obf.s -o main
Let's use the following source code as an example to obfuscate:
#include <stdio.h>
short zero[2] = {0,1};
static short *d(void){
return zero;
}
static short c(int x){
if(x == 0)
return (*(d()+1) ^ 12);
return c(x-1)+1;
}
static int b(int x){
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < x; i++){
sum += c(i);
}
return sum;
}
static void a(unsigned long long x){
for(int i = 0; i < x; i++){
int temp = b(i) + 1;
printf("%d ", temp);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
int i;
if(argc > 1){
sscanf(argv[1], "%d", &i);
a(i);
}
return 0;
}Substitute some basic binary operators (e.g. xor, add) with functions.
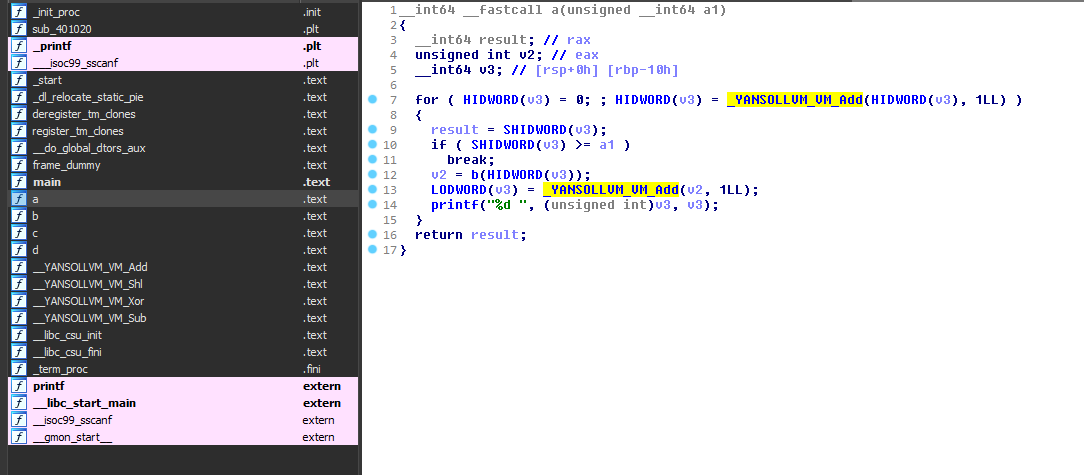
This pass merges all internal linkage functions (e.g. static function) to a single function.
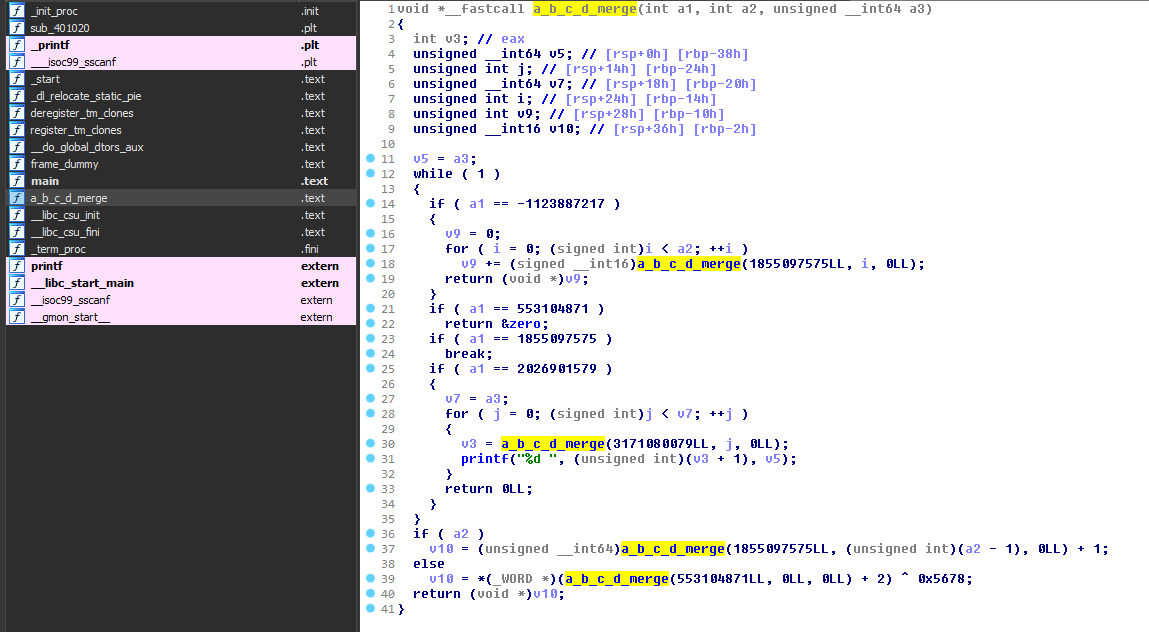
Based on OLLVM's CFG flattening, but it seperates the internal state transfer and the switch variable using a simple hash function.

Similar to OLLVM's bogus control flow, but totally different. It splits basic blocks and uses switch to add false branches among them.
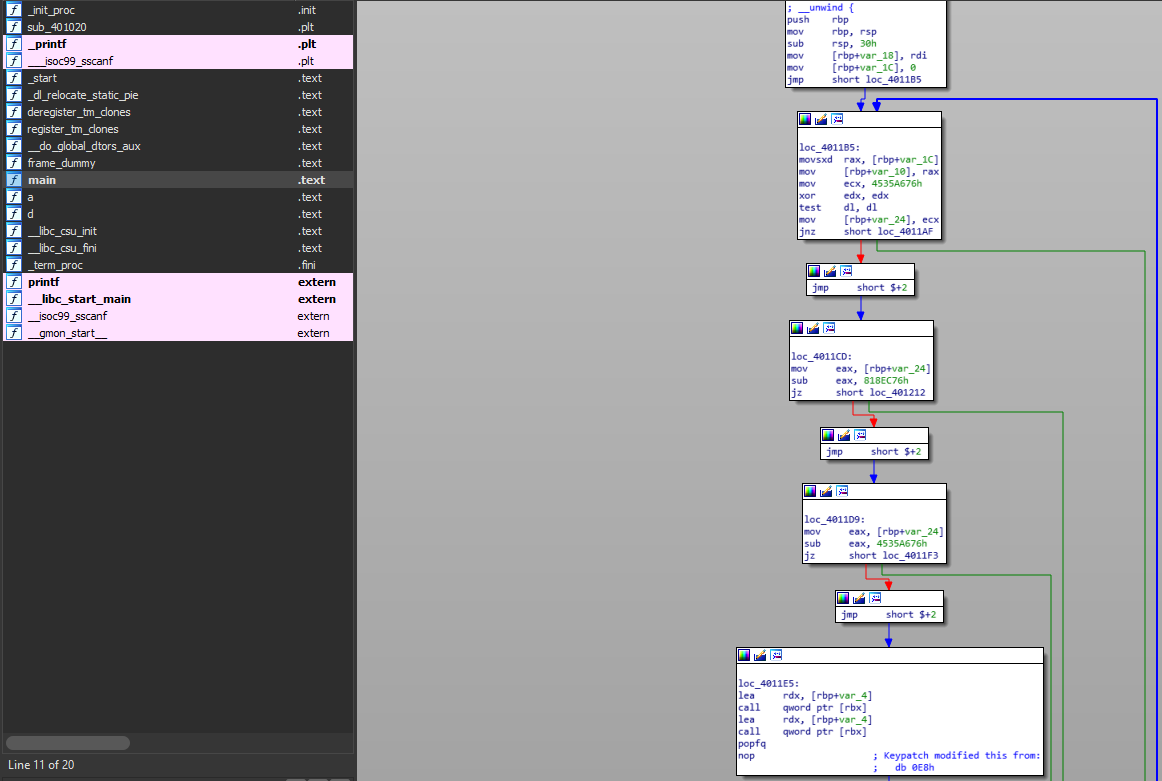
 IDA cannot show CFG due to some garbage code. After patching them:
IDA cannot show CFG due to some garbage code. After patching them:
Obfuscate constants using MBA. The Flattening and Connect passes will need this otherwise the almighty compiler optimizer will optimize away all false branches.

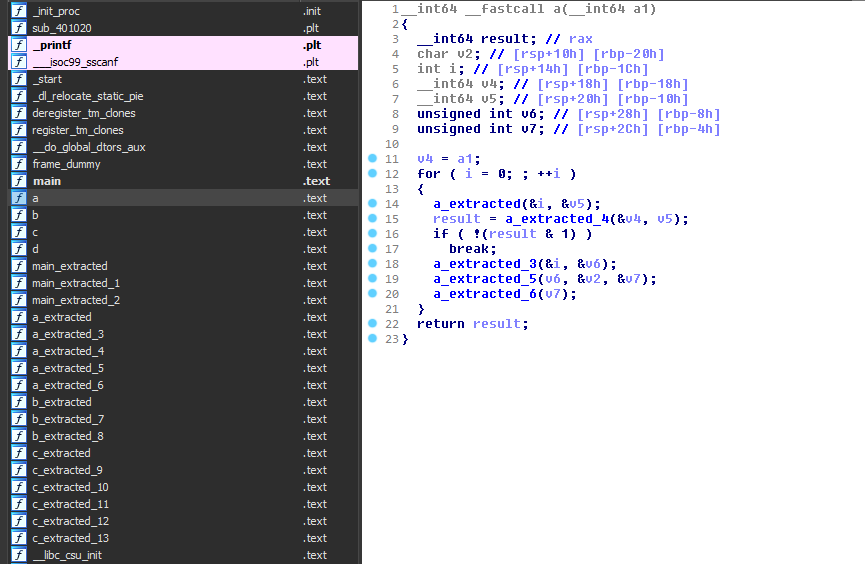
Split & extract some basic blocks and make them new functions.
Obfuscate all internal linkage functions calls by using randomly generated calling conventions.

The CFG after enabling all above passes:

No warrant. Only bugs. Use at your own risk.
Partial code of Flattening.cpp comes from the original OLLVM project, which is released under the University of Illinois/NCSA Open Source License.
Partial code of ObfuscateConstant.cpp comes from the Quarkslab/llvm-passes, which is released under the MIT License.
Besides, the X86 related code is modified directly from the LLVM, which is released under the Apache-2.0 WITH LLVM-exception License.
All other files are my own work.
The whole project is released under GPLv3 which is surely compatible with all above licenses.