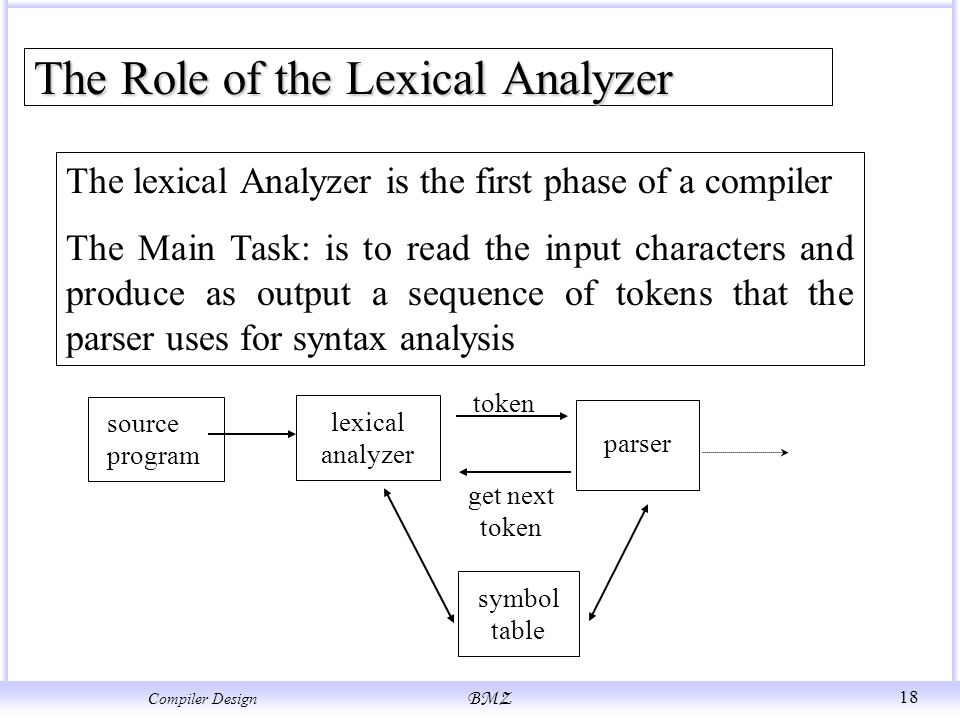
- The lexer efficiently tokenizes C code, recognizing keywords, identifiers, operators, constants, and preprocessor directives.
- The lexer has a preprocessor which handles comments and preprocessor directives.
- The lexer efficiently handles various operator types (arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, and ternary), along with character constants, string literals, and invalid characters.
- Output Formatting: Tokens are formatted for output, including their type and lexeme.
- Effective Use of Standard Library: The code leverages various components from the C++ Standard Library, including string manipulation (), input/output operations (), and data structures (, <unordered_set>, <unordered_map>). This showcases the power and efficiency of utilizing standard library features for common programming tasks.
- Assertions for Testing and Debugging: The inclusion of assertions (assert) in the test cases ensures the correctness of the lexer's behavior during testing. Assertions help detect unexpected conditions and provide valuable feedback for debugging, contributing to the reliability and stability of the codebase.
- Object Oriented Design: The lexer and its classes embrace object-oriented principles, ensuring readable, maintainable, and modular code. Core concepts like encapsulation and polymorphism are demonstrated through classes such as Token and Lexer, promoting code reusability and facilitating easier maintenance and testing.
- C++ Compiler
- A Build system
- Clone the project
https://github.com/vivekkdagar/c-lexical-analyzer- Navigate to the Project Directory
cd c-lexical-analyzer- Install dependencies: Ensure C++ Compiler and a build system is installed
- Build the project using your preferred build system (I used CMake)
- Execute main.cpp. You can change the text in the input string of main.cpp to tokenize different code
- What is the purpose of the Token class?
- The Token class represents a lexical token in the C/C++ code. It encapsulates information about the token type and its corresponding lexeme.
- How are tokens categorized in the lexer?
- Tokens are categorized into different types such as keywords, identifiers, constants, operators, and special symbols. The lexer analyzes the input code and assigns appropriate token types based on predefined rules.
- How does the lexer handle invalid characters or tokens?
- If the lexer encounters invalid characters or tokens, it categorizes them as INVALID_TOK and includes them in the token stream. These tokens can be identified and handled appropriately during further processing.
- What is lexical analysis, and why is it important in compiler design?
- Lexical analysis, also known as scanning or tokenization, is the first phase of the compilation process. It involves breaking the input code into a sequence of tokens representing the language's fundamental elements. Lexical analysis is crucial as it provides a structured representation of the source code, which facilitates further processing by subsequent phases of the compiler.
- How does the lexer handle whitespace and comments in the input code?
- The lexer typically skips over whitespace characters such as spaces, tabs, and newline characters. It also recognizes and ignores comments, ensuring that they do not contribute to the token stream. By discarding whitespace and comments, the lexer focuses on extracting meaningful tokens from the code.
- Can the lexer handle complex tokenization scenarios, such as string literals or nested expressions?
- Yes, the lexer is designed to handle various tokenization scenarios encountered in real-world programming languages. It can accurately tokenize string literals, character constants, and handle nested expressions or control structures. The lexer's robust design ensures that it can effectively parse complex code constructs while maintaining efficiency and accuracy.
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for more information.
Vivek Dagar - - [email protected]
Project Link: https://github.com/vivekkdagar/c-lexical-analyzer