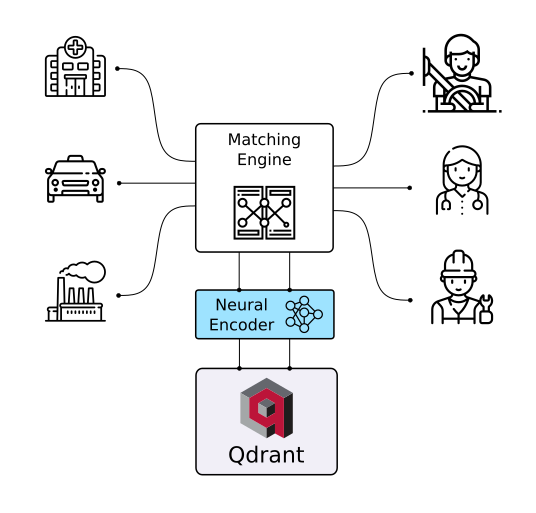
Vector Similarity Search Engine with extended filtering support
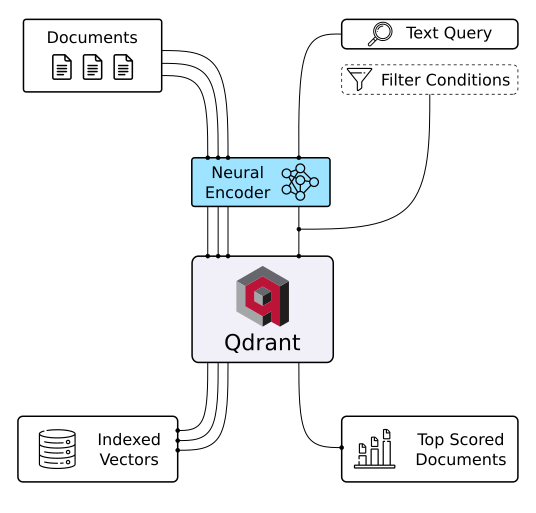
Qdrant (read: quadrant ) is a vector similarity search engine. It provides a production-ready service with a convenient API to store, search, and manage points - vectors with an additional payload. Qdrant is tailored to extended filtering support. It makes it useful for all sorts of neural-network or semantic-based matching, faceted search, and other applications.
Qdrant is written in Rust 🦀, which makes it reliable even under high load.
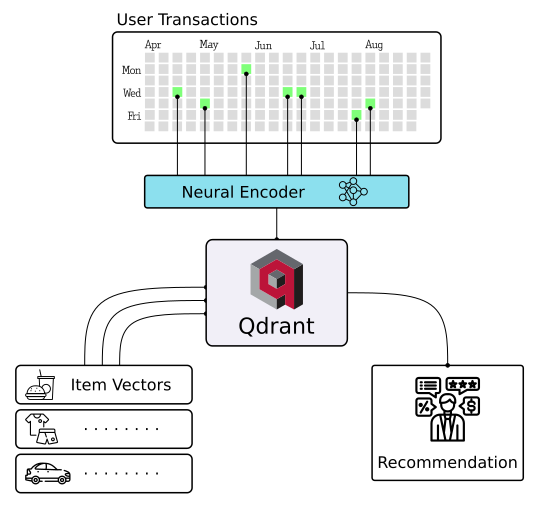
With Qdrant, embeddings or neural network encoders can be turned into full-fledged applications for matching, searching, recommending, and much more!
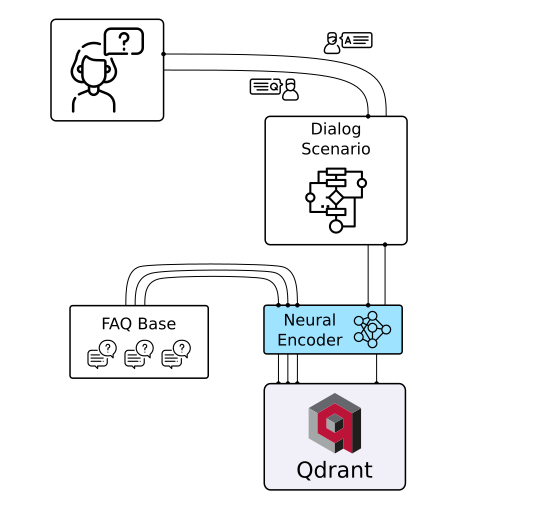
The neural search uses semantic embeddings instead of keywords and works best with short texts. With Qdrant and a pre-trained neural network, you can build and deploy semantic neural search on your data in minutes. Try it online!
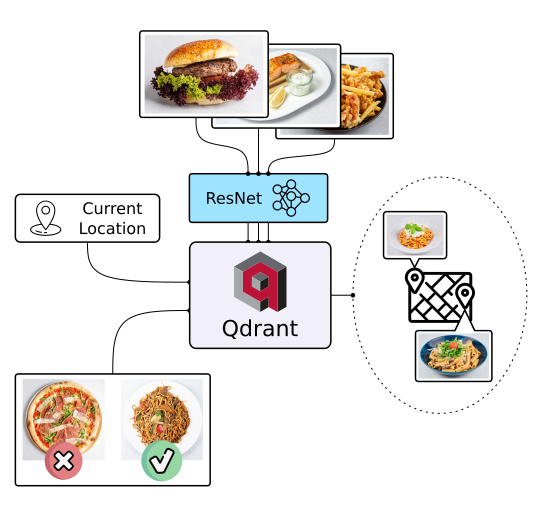
There are multiple ways to discover things, text search is not the only one. In the case of food, people rely more on appearance than description and ingredients. So why not let people choose their next lunch by its appearance, even if they don’t know the name of the dish? Check it out!
Online OpenAPI 3.0 documentation is available here. OpenAPI makes it easy to generate client for virtually any framework or programing language.
You can also download raw OpenAPI definitions.
Qdrant supports key-value payload associated with vectors. Not only stores payload but also allows filter results based on payload values.
It allows any combinations of should, must and must_not conditions, but unlike ElasticSearch post-filtering, Qdrant guarantees all relevant vectors are retrieved.
Vector payload supports a large variety of data types and query conditions, including string matching, numerical ranges, geo-locations, and more. Payload filtering conditions allow you to build almost any custom business logic that should work on top of similarity matching.
Using the information about the stored key-value data, query planner decides on the best way to execute the query.
For example, if the search space limited by filters is small, it is more efficient to use a full brute force than an index.
With the BLAS library, Qdrant can take advantage of modern CPU architectures.
It allows you to search even faster on modern hardware.
Once service confirmed an update - it won't lose data even in case of power shut down. All operations are stored in the update journal and the latest database state could be easily reconstructed at any moment.
Qdrant does not rely on any external database or orchestration controller, which makes it very easy to configure.
Build your own from source
docker build . --tag=qdrantOr use latest pre-built image from DockerHub
docker pull generall/qdrantTo run container use command:
docker run -p 6333:6333 \
-v $(pwd)/path/to/data:/qdrant/storage \
-v $(pwd)/path/to/custom_config.yaml:/qdrant/config/production.yaml \
qdrant/qdrant/storage- is a place where Qdrant persists all your data. Make sure to mount it as a volume, otherwise docker will drop it with the container./qdrant/config/production.yaml- is the file with engine configuration. You can override any value from the reference config
Now Qdrant should be accessible at localhost:6333
- The best place to start is Quick Start Guide
- Use the OpenAPI specification as a reference
- Follow our Step-by-Step Tutorial to create your first neural network project with Qdrant
- Join our Telegram group
- Follow us on Twitter
- Subscribe to our Newsletters
- Write us an email [email protected]
Qdrant is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. View a copy of the License file.